
Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 8-K
Exhibit 99.02

© 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Live Virus Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine Presentation to World Vaccine & Immunotherapy Congress Version 1123 December 1, 2022 (Doc 0392)

2 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 2 Cautionary Note on Forward - Looking Statements Certain statements in this presentation regarding strategic plans, expectations and objectives for future operations or results are “forward - looking statements” as defined by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be identified by the use of forward - looking words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “forecast,” “estimate” and “intend,” among others. These forward - looking statements are based on Tonix’s current expectations and actual results could differ materially. There are a number of factors that could cause actual events to differ materially from those indicated by such forward - looking statements. These factors include, but are not limited to, the risks related to failure to obtain FDA clearances or approvals and noncompliance with FDA regulations; delays and uncertainties caused by the global COVID - 19 pandemic; risks related to the timing and progress of clinical development of our product candidates; our need for additional financing; uncertainties of patent protection and litigation; uncertainties of government or third party payor reimbursement; limited research and development efforts and dependence upon third parties; and substantial competition. As with any pharmaceutical under development, there are significant risks in the development, regulatory approval and commercialization of new products. The forward - looking statements in this presentation are made as of the date of this presentation, even if subsequently made available by Tonix on its website or otherwise. Tonix does not undertake an obligation to update or revise any forward - looking statement, except as required by law. Investors should read the risk factors set forth in the Annual Report on Form 10 - K for the year ended December 31, 2021, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on March 14, 2022, and periodic reports and current reports filed with the SEC on or after the date thereof. All of Tonix's forward - looking statements are expressly qualified by all such risk factors and other cautionary statements.

3 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 3 Live Virus Vaccines: Development Rationale • Control of smallpox, measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox and other viral conditions − Prevent forward transmission • Effective in eliciting durable or long - term immunity • Economical to manufacture at scale − Low dose because replication amplifies dose in vivo − Single shot administration • Standard cold chain required for shipping and storage • Live virus vaccines are the oldest vaccine technology − Starting with Edward Jenner’s smallpox vaccine, the first vaccine, eradicated smallpox INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO

4 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 4 First Live Virus vaccine: Edward Jenner’s Inquiry 1 (1796) – 1/2 “There is a disease to which the Horse from his state of domestication is frequently subject. The Farriers have termed it the Grease . It is an inflammation and swelling in the heel, from which issues matter 2 possessing properties of a very peculiar kind, which seems capable of generating a disease in the Human Body (after it has undergone the modification 3 I shall presently speak of), which bears so strong a resemblance to the Small Pox, that I think it highly probable it may be the source of that disease.” INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Jenner, E. “An Inquiry Into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae , a Disease Discovered in Some of the Western Counties of England, Particularly Gloucestershire, and Known by the Name of the Cow Pox (p 2 - 3.) 2 Vaccine virus 3 Passage in cows

5 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 5 First Live Virus vaccine: Edward Jenner’s Inquiry 1 (1796) – 2/2 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Jenner, E. “An Inquiry Into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae , a Disease Discovered in Some of the Western Counties of England, Particularly Gloucestershire, and Known by the Name of the Cow Pox (p 3.) “In this Dairy Country a great number of Cows are kept, and the office of milking is performed indiscriminately by Men and Maid Servants. One of the former having been appointed to apply dressings to the heels of a Horse affected with the Grease , and not paying due attention to cleanliness, incautiously bears his part in milking the Cows, with some particles of the infectious matter adhering to his fingers. When this is the case, it commonly happens that a disease is communicated to the Cows, and from the Cows to the Dairy - maids, which spreads through the farm until most of the cattle and domestics feel its unpleasant consequences. The disease has obtained the name of the Cow Pox .”

6 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 6 Loy’s “ Account of some experiments 1 (1801) “This fact induces me to suspect, that two kinds of Grease exist, differing from each other in the power of giving disease to the human or brute animal: and there is another circumstance which renders this supposition probable. The horses that communicated the infection to their dressers, were affected with a general, as well as a topical, disease. The animals, at the commencement of their disease, were evidently in a feverish state, from which they were relived as soon as the complaint appeared at their heels, and an eruption upon their skin. The horse , too, from whom the infectious matter was procured for inoculation, had a considerable indisposition, previous to the disease at his heels, which was attended, as in the others, with an eruption over the greatest part of his body: but those that did not communicate the diseases at all, had a local affection only.” INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Loy JG. An account of some experiments on the origin of the cow - pox: Whitby; 1801. (p 20 - 21.)
7 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 7 Equination 1 : Use of Smallpox Vaccines from Horse Lesions • Both Jenner and Loy used vaccine from horses; subsequently “ Equination ” was used in Europe in parallel with “vaccination” − Jenner believed that his “cowpox” or “vaccinia” came from horses with “Grease” • Producers of “vaccinia” may have supplemented or refreshed stocks with horsepox periodically” − Methods of propagating vaccine in the 19 th Century were not based on understanding of microbiology • Horsepox isolated from a sick horse in Mongolia in 1976 − Like many other poxviruses, natural host is likely rodents (mice or voles) − No cases reported in >30 years, some believe it to be extinct; eliminated through improved animal husbandry INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Esparza J, Schrick L, Damaso CR, Nitsche A. Equination (inoculation of horsepox): An early alternative to vaccination (inoculation of cowpox) and the potential role of horsepox vir us in the origin of the smallpox vaccine. Vaccine . 2017 Dec 19;35(52):7222 - 7230. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Review. PMID:29137821

8 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 8 Horsepox: Development Rationale • Horsepox clone sequenced in 2006 shares a common ancestor with vaccinia and could be considered a strain of vaccinia − Similar to cowpox with “intact” inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) – could be considered a primordial strain of vaccinia • U.S. vaccine from Mulford 1902 was found to be 99.7% similar to horsepox in core viral sequence 1,2 − TNX - 1800 has 99.7% colinear identity with circa 1860 smallpox vaccine 2,3 − Strong evidence linking a horsepox - like virus as progenitor to modern vaccinia − Effectiveness of older vaccines support belief that horsepox will e protective against smallpox • Genetic analysis of early vaccines indicates that “horsepox” is closely related to Edward Jenner’s vaccinia from 1796 − Modern “vaccinia” evolved during the 220 years it was propagated by primitive methods – for over 120 years before “viruses” were identified − Prevents forward transmission − Edward Jenner’s “cowpox”/”vaccinia” smallpox vaccine eradicated smallpox INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Schrick, L. et al An Early American Smallpox Vaccine Based on Horsepox N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1491 2 Tulman ER, et al. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol ; 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 3 Brinkmann A et al, Genome Biol ogy 2020 ; 21:286 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059 - 020 - 02202 - 0
9 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 9 Horsepox Compared to Cowpox and Vaccinia Strains 1 Consistent with Near “Primordial” Strain Status 1 Evans, D. U. of Alberta (2018) with permission
10 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 10 Certain Gene Factors Have the Potential to Enhance Virulence of Vaccinia and Cowpox Relative to Horsepox Replicative capacity equates to the ”fitness” or competitive advantage of the virus *This is a conceptual view to illustrate whether these genes are active or not and does not indicate the actual number, size, or location of the genes † Stripes indicate regions among different vaccinia strains that are present in some but absent in others 1 Schrick L, et al. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(15):1491 - 1492. 2 Dabrowski PW, et al. PLoS One . 2013;8(12):e79953. 3 Tulman ER, et al. J Virol. 2006;80(18):9244 - 9258. 4 Qin L, et al. J Virol. 2015;89(3):1809 - 1824. Virulence gene factors* Modern cowpox † Robust replicative capacity; wide host range 3 Horsepox Attenuated replicative capacity; host range unknown 1,2 Robust replicative capacity; wide host range 4 Modern vaccinia † Virulence genes active in modern cowpox and vaccinia 3,4 Virulence gene factors* Virulence genes inactivated in HPXV 1,2
11 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 11 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO Historical Safety Spectrum Of Pox - based Vectors Optimizing Live Virus Vaccines Very safe but high dosing ~1 death per million ~10 deaths per million Nonreplicating Poor Transgene immunogenicity Robust Replication Risk for adverse vaccination events Parental smallpox vaccines Dryvax Lister TianTan Copenhagen Tashkent MVA Canarypox Fowlpox Δ J2R Δ F4L Δ J2R Optimal Replicative Capacity (“sweet spot”) New Recombinant Pox VACCINE (RPV) Intermediate Replicative Capacity Ability to elicit robust immunological responses to Transgene
12 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 12 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO Commercial Applications of Licensed Recombinant Poxvirus - Based Vaccines 1 Taylor J, et al. Avian Dis. 1996;40(1):173 - 180. 2 The Poultry Site. March 14, 2005. Accessed July 9, 2021. https://www.thepoultrysite.com/news/2005/03/merial - launches - new - h5n1 - av ian - influenza - vaccine - provides - new - hope - for - avian - flu - epidemic 3 Boehringer Ingelheim. Accessed July 9, 2021. https://www.boehringer - ingelheim.com/animal - health/companion - animals - products/purev ax 4 Larson LJ, et al. Vet Ther. 2007;8(2):101 - 106. • Newcastle disease virus (NDV) TROVAC ( recombinant fowlpox ) • Avian influenza (AIV) TROVAC ( recombinant fowlpox ) (H5N9 and H5N1) Agriculture 1,2 • Recombinant canarypox rabies vaccine (ALVAC - RG) and feline leukemia (ALVAC - FeLV) Cats 3 • RECOMBITEK ® C4 recombinant canarypox vector expressing the HA and F glycoproteins of canine distemper virus; modified live adenovirus type 2, parainfluenza virus, and parvovirus Dogs 4
13 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 13 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO Approved Recombinant Poxvirus - Based Commercial Products 1 - 3 Product Application / disease Location Poxvirus vector Host restricted? Doses released to environment TROVAC - AIV H5N1 Boehringer Ingelheim Agriculture/avian influenza Mexico, Central America TROVAC - AIV H5N1 No Replication competent 2 billion (as of 2006) Purevax FeLV Boehringer Ingelheim Companion animals (cats)/FeLV US, others ALVAC - FeLV Gag/Pol Yes Replication incompetent Unknown Purevax Rabies Boehringer Ingelheim Companion animals (cats)/rabies US, others ALVAC - RG Yes Replication incompetent Unknown Recombitek Boehringer Ingelheim Companion animals (dogs)/canine distemper US, others ALVAC - HA, F Yes Replication incompetent Unknown Raboral V - RG Rabisin Boehringer Ingelheim Wildlife control of rabies US, Europe, Israel Vaccinia Copenhagen RG No Replication competent 250 million doses 5 million doses/year 1 Boehringer Ingelheim. Accessed July 15, 2021. https://www.boehringer - ingelheim.com/animal - health/products 2 Bublot M, Pritchard N, Swayne DE, et al. Development and use of fowlpox vectored vaccines for avian influenza. Ann N Y Acad Sci . 2006;1081:193 - 201. 3 Maki J, Guiot AL, Aubert M, et al. Oral vaccination of wildlife using a vaccinia - rabies - glycoprotein recombinant virus vaccine (RABORAL V - RG ® ): a global review. Vet Res . 2017;48(1):57.
14 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 14 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO Environmental Distribution: Vaccinia Released Aerially as Rabies Vaccine • RABORAL V - RG ® is an oral vaccine based on vaccinia – rabies - glycoprotein recombinant virus used to prevent the spread of rabies among wildlife populations 1 - 3,* − RABORAL has been in continuous use since 1987 − Approximately 250 million doses in the form of animal baits have been aerially distributed across Europe, Israel, Canada, and the US at a rate of about 5 million baits per year − Species targeted include skunks, racoons, foxes, and coyotes − Jordona Kirby, the rabies field coordinator for the USDA's National Rabies Management Program was interviewed about dropping Raboral out of low - flying planes and helicopters to control rabies in the East Coast of the US 4 * A registered trademark of Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health 1 Raboral V - RG ® . Accessed July 9, 2021. https://www.raboral.com/about - rabies/raboral - v - rg 2 Kieny MP, et al. Nature. 1984;312(5990):163 - 166. 3 Maki J, et al. Vet Res. 2017;48(1):57. 4 Science Friday : NPR Sept 30, 2022 NPR’s program “Science Friday” at 30:02 in the podcast www.npr.org/podcasts/583350334/science - friday
15 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 15 TNX - 801 (Live HPXV for Percutaneous Administration) • Vaccine based on sequence of isolated horsepox (HPXV) clone 1 − Synthesized 2 since 1976 isolate was not available outside of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) − No new gene elements − Coding sequence identical to HPXV • Small plaque size in culture − Appears identical to CDC publication of 1976 horsepox isolate 3 • Substantially decreased virulence in mice 2 and efficacy in NHPs to protect against monkeypox 4 − Non - human primate study showing protection from monkeypox presented at 2020 ASM Biothreats conference INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Tulman ER, et al. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol . 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 2 Noyce RS, et al.. Construction of an infectious horsepox virus vaccine from chemically synthesized DNA fragments. PLoS One . 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0188453 3 Trindade GS , et al. Serro 2 Virus Highlights the Fundamental Genomic and Biological Features of a Natural Vaccinia Virus Infecting Humans. Viruses 2016 Dec 10;8(12). pii : E328. PMID:27973399 PMCID: PMC5192389 DOI: 10.3390/v8120328 4 Noyce, RS, et al. Synthetic Chimeric Horsepox Virus ( scHPXV ) Vaccination Protects Macaques from Monkeypox* Presented as a poster at the American Society of Microbiology BioThreats Conference - January 29, 2020, Arlington, VA . ( https://content.equisolve.net/tonixpharma/media/10929ac27f4fb5f5204f5cf41d59a121.pdf )
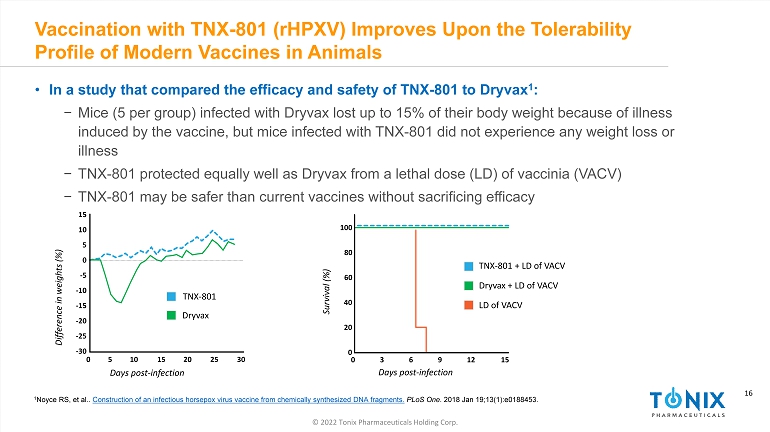
16 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 16 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO Vaccination with TNX - 801 ( rHPXV ) Improves Upon the Tolerability Profile of Modern Vaccines in Animals • In a study that compared the efficacy and safety of TNX - 801 to Dryvax 1 : − Mice (5 per group) infected with Dryvax lost up to 15% of their body weight because of illness induced by the vaccine, but mice infected with TNX - 801 did not experience any weight loss or illness − TNX - 801 protected equally well as Dryvax from a lethal dose (LD) of vaccinia (VACV) − TNX - 801 may be safer than current vaccines without sacrificing efficacy 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 Days post - infection Survival (%) TNX - 801 + LD of VACV Dryvax + LD of VACV LD of VACV 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 15 10 5 0 - 5 - 10 - 15 - 20 - 25 - 30 Days post - infection Difference in weights (%) TNX - 801 Dryvax 1 Noyce RS, et al.. Construction of an infectious horsepox virus vaccine from chemically synthesized DNA fragments. PLoS One . 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0188453.
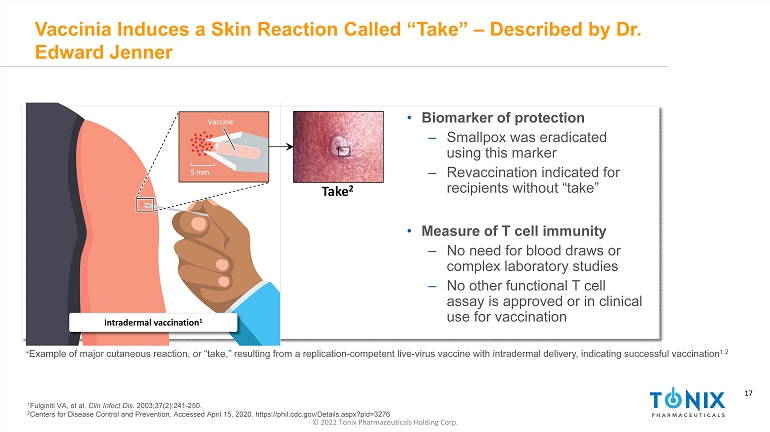
17 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 17 Vaccinia Induces a Skin Reaction Called “Take” – Described by Dr. Edward Jenner * Example of major cutaneous reaction, or “take,” resulting from a replication - competent live - virus vaccine with intradermal deliv ery, indicating successful vaccination 1,2 5 mm Vaccine Intradermal vaccination 1 Take 2 • Biomarker of protection ‒ Smallpox was eradicated using this marker ‒ Revaccination indicated for recipients without “take” • Measure of T cell immunity ‒ No need for blood draws or complex laboratory studies ‒ No other functional T cell assay is approved or in clinical use for vaccination 1 Fulginiti VA, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(2):241 - 250. 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed April 15, 2020. https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=3276 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO
18 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 18 No Overt Clinical Signs Observed in TNX - 801 Vaccinated Macaques After Monkeypox (MPVX) Challenge 1 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND IMMUNOLOGY PORTFOLIO 1 Noyce, RS, et al. Synthetic Chimeric Horsepox Virus ( scHPXV ) Vaccination Protects Macaques from Monkeypox* Presented as a poster at the American Society of Microbiology BioThreats Conference - January 29, 2020, Arlington, VA . ( https://content.equisolve.net/tonixpharma/media/10929ac27f4fb5f5204f5cf41d59a121.pdf ) No monkeypox lesions observed after monkeypox (MPXV) challenge in any of the eight animals vaccinated with TNX - 801 Legend : Cynomolgus macaques (4 per group), were vaccinated via scarification using a bifurcated needle. Two different doses of TNX - 801 ( scHPXV ) vaccine were tested (panel a. and b.); one dose of TNX - 1200 ( sVACV )(panel c.); or vehicle (panel d). After monkeypox (MPXV) challenge, no lesions were seen in any of the 8 animals vaccinated wi th TNX - 801 (panel a and b.). One animal in the TNX - 1200 arm died from unrelated causes, and two of three remaining animals showed lesions by Day 69 (panel c.). All fou r vehicle vaccinated animals developed lesions (panel d.) Clinical signs of systemic monkeypox infections were seen in all 4 vehicle - vaccinated animals (panel d.) by Day 69, but TNX - 801 and TNX - 1 200 vaccinated animals were protected. In Panels a - d, blue symbols are male animals and red are female. Methods : 4 of 4 animals in the 4x10 6 PFU dose, and 3 of 4 animals in the 5x10 5 PFU dose groups exhibited a “take” at Day 7 after a single vaccination. A take is a biomarker of protective immunity. In the TNX - 1200 ( sVACV ) arm only 1 of 4 animals exhibited a take after a single vaccination. The animals that did not present a take were revaccina ted on Day 14: the one TNX - 801 animal was revaccinated with 5x10 5 PFU TNX - 801 and the 3 TNX - 1200 animals were revaccinated with 2.4x10 5 PFU TNX - 1200. All but one of the TNX - 1200 animals subsequently produced a take. Tolerability was comparable for TNX - 801 and TNX - 1200.

19 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 19 Monkeypox Outside of Africa • First case reported May 7th, more than 25,000 cases observed outside of Africa 1 − West African strain found outside of Africa, low mortality in Africa (<1%) − Mortality in Africa believed to be 3 - 6%; strain prevalent in Congo has higher mortality (~10%) − Skin to skin transmission − In latest outbreak most cases outside Africa were linked to linked to a events in Spain and Belgium − Last outbreak outside of Africa was 2003 when infected prairie dogs led to 70 cases in the US • Resurgence believed due to cessation of routine smallpox vaccination − Smallpox vaccination with live virus vaccinia protects against monkeypox 2 • US Stockpile includes Jynneos® 3 , 2 - dose regimen of non - replicating MVA vaccinia strain that protects NHPs from monkeypox 4 − US has ordered more Jynneos – CDC considering ring vaccination and vaccinating first responders, but Jynneos requires two dose regimen − ACAM2000® 3 - live replicating 1 - dose regimen also recommended but not FDA approved 1 The Economist May 25th 2022, ”Monkeypox is not covid mk2, but it needs to be nipped in the bud: The illness can be dangerous for children, pr egnant women and the immunocompromised”: URL: Monkeypox is not covid mk2, but it needs to be nipped in the bud | The Economist 2 https://www.cdc.gov/smallpox/pdfs/revaccination - memo.pdf 3 Jynneos is a trademark of Bavarian Nordic and ACAM2000 is trademark of Emergent BioSolutions 4 Rao, AK. et al. May 27, 2022. US CDC MMWR 71 “Use of JYNNEOS (Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine, Live, Nonreplicating) for Preex pos ure Vaccination of Persons at Risk for Occupational Exposure to Orthopoxviruses : Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2022” www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7122e1.htm?s_cid=mm7122e1_w
20 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 20 Live Virus Vaccine Platform: Recombinant Pox Vaccine (RPV) Technology for Emerging Infectious Diseases and Oncolytics Monkeypox and Smallpox Future Pandemics & New Infectious Diseases COVID - 19 Biodefense Using Proven Science To Address Challenging Disease States, We Have Created A Programmable Technology Platform Aimed At Combating Future Threats To Public Health Vaccinia Horsepox ANTIGEN CODING Oncology RPV VECTOR BELIEVED SIMILAR TO EDWARD JENNER’S VACCINE 1 - 3 1 Shrick, L. N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1491 - 1492. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc1707600 2 Esparza, J. Vaccine . 2020 Jun 19; 38(30): 4773 – 4779. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.037 3 Brinkmann, A. Genome Biol . 2020; 21: 286. doi : 10.1186/s13059 - 020 - 02202 - 0

21 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 21 Live Virus RPV P latform Internal Development & Manufacturing Capabilities Infectious Disease R&D Center (RDC) – Frederick, MD • Function : Accelerated development of vaccines and antiviral drugs against COVID - 19, its variants and other infectious diseases • Description : ~48,000 square feet, BSL - 2 with some areas designated BSL - 3 • Status : Operational Advanced Development Center (ADC) – North Dartmouth, MA • Function : Development and clinical scale manufacturing of biologics • Description : ~45,000 square feet, BSL - 2 • Status : Operational Commercial Manufacturing Center (CMC) – Hamilton, MT • Function : Phase 3 and Commercial scale manufacturing of biologics • Description : ~44 acre green field site, planned BSL - 2 • Status : Planning for site enabling work Architectural Rendering

22 © 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 22 Investigators and Collaborators Tonix • Seth Lederman • Siobhan Fogarty • Sina Bavari • Scott Goebel • Bruce Daugherty • Helen Stillwell 1 Univ. of Alberta • Ryan Noyce • David Evans Univ. of Maryland – Institute of Human Virology • José Esparza Southern Research • Fusataka Koide • Landon Westfall 2 • Karen Gilbert 3 LINQ Pharma Consulting • Onesmo Mpanju Current Addresses 1 University of Pennsylvania 2 IITRI 3 National Toxicology Program (NTP) at National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), NIH; Artic Slope Regional C orp .

© 2022 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. THANK YOU