
TONIX PHARMACEUTICALS HOLDING CORP. FORM 8-K
Exhibit 99.02

Primary vs Secondary Sex Hormones and Migraine 1

Disclosures 2 Professor David C Yeomans, Director of Pain Research, Stanford Medical School • SiteOne Therapeutics – Founder • NewBio – Founder • Tonix Pharmaceuticals - Consultant • Nalu Medical – SAB chair • Cytonics – SAB chair • Circuit Therapeutics – Consultant • Endo Pharmaceuticals - Consultant

Sex Hormones 3 Sex hormones are critical regulators of sex - related characteristics and behaviors Primary: • Progesterone • Estrogens • Androgens Secondary: • Prolactin • Oxytocin
The “Estrogen withdrawal hypothesis”, developed by Somerville and colleagues in 1972, postulates that attacks of menstrual migraine are triggered by the decrease in estrogen levels preceding menstruation. Hypothesized pathology: • A drop in estrogen may cause an increased sensitivity to prostaglandins and a release of neuropeptides such as CGRP, substance P and neurokinins which could result in neurogenic inflammation. • This physiological response provokes alterations in the microvasculature of the dura mater, changes in calcium and magnesium concentrations, and an imbalance in serotonin and dopamine concentrations 4 Estrogens and Migraine

However, estrogens are generally ineffective in in migraine prevention RCTs 5 RCT (35 pts): Percutaneous Estradiol reduced migraine frequency by 22% compared to placebo but increased migraines as soon as drug stopped (MacGregor et al., 2006) RCT (27 pts): Percutaneous Estradiol no significant effect vs. placebo (Almén - Christensson et al. 2011). Estradiol and progesterone RCT (50 pts) Percutaneous or oral estradiol plus progesterone: significantly worsened migraine with aura (Nappi et al, 2001). RCT (22 pts) Percutaneous estradiol significantly v placebo, reduced frequency of menstrual migraine (Dennerstein et al., 1988).
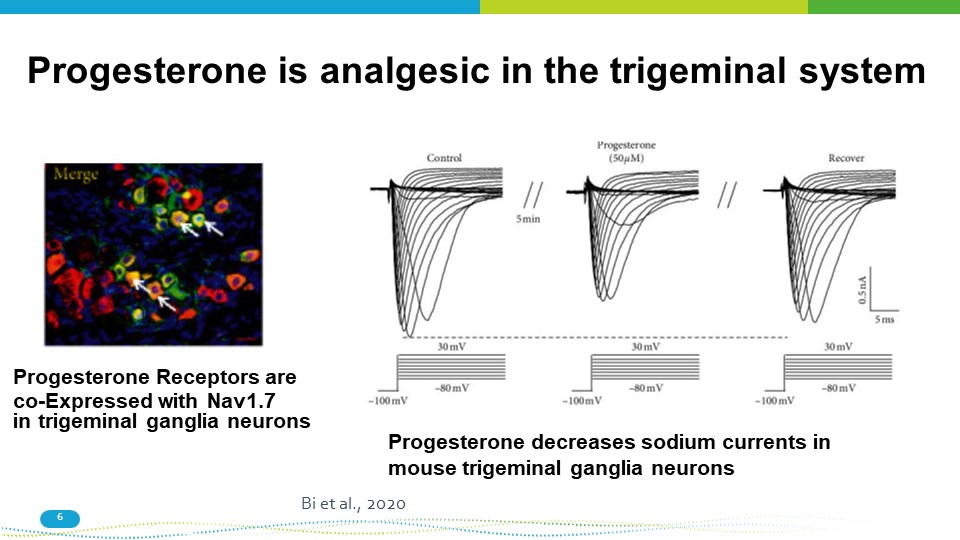
Progesterone is analgesic in the trigeminal system Progesterone Receptors are co - Expressed with Nav1.7 in trigeminal ganglia neurons Progesterone decreases sodium currents in mouse trigeminal ganglia neurons Bi et al., 2020 6
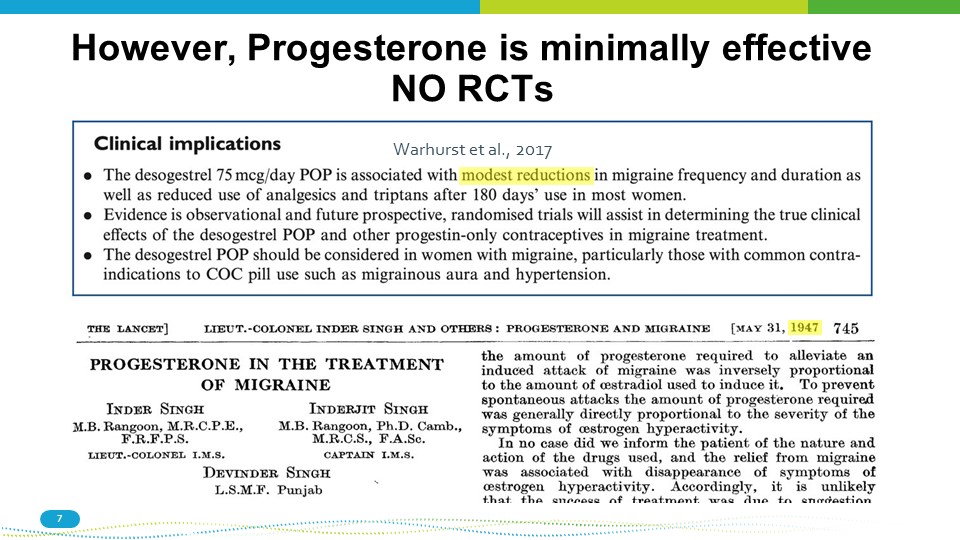
However, Progesterone is minimally effective NO RCTs Warhurst et al., 2017 7

Testosterone 8 No RCT but pilot study showing strong effects of testosterone implant on 27 female migraineurs with symptoms of androgen insufficiency . Compared to pre - treatment, testosterone produced a significant decrease in migraine severity with 74 % reporting severity scores of zero (Glaser et al . , 2012 ) .
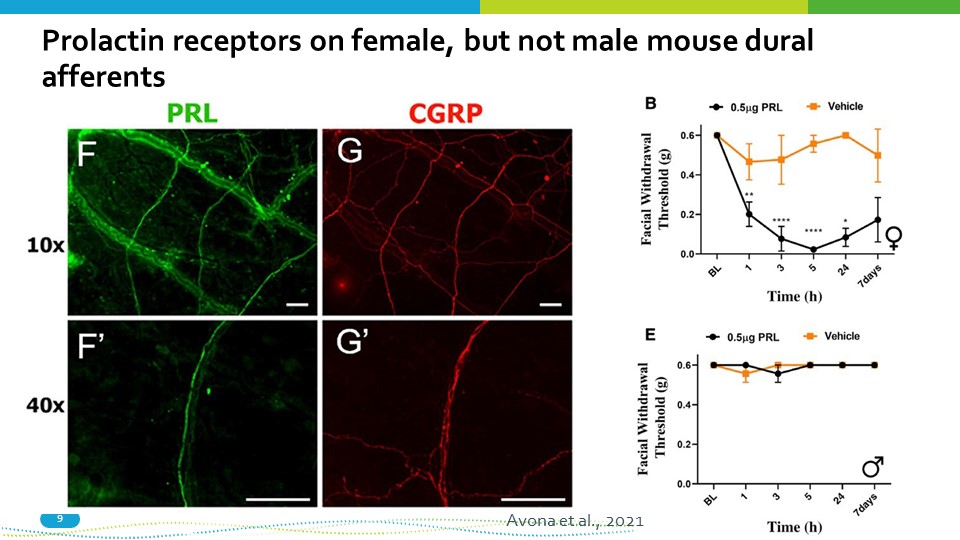
Prolactin receptors on female, but not male mouse dural afferents 9 Avona et al., 2021
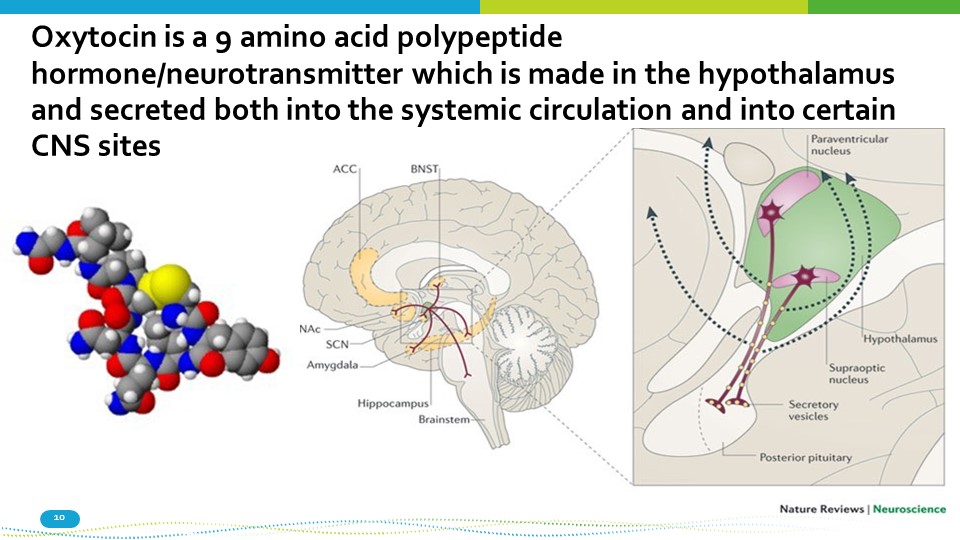
Oxytocin is a 9 amino acid polypeptide hormone/neurotransmitter which is made in the hypothalamus and secreted both into the systemic circulation and into certain CNS sites 10
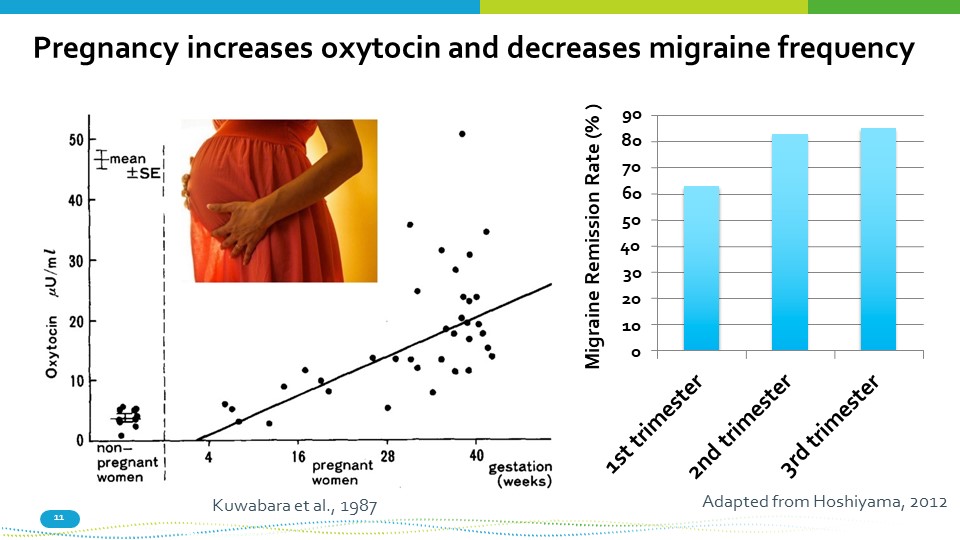
Pregnancy increases oxytocin and decreases migraine frequency 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Migraine Remission Rate (% ) Adapted from Hoshiyama, 2012 Kuwabara et al., 1987 11
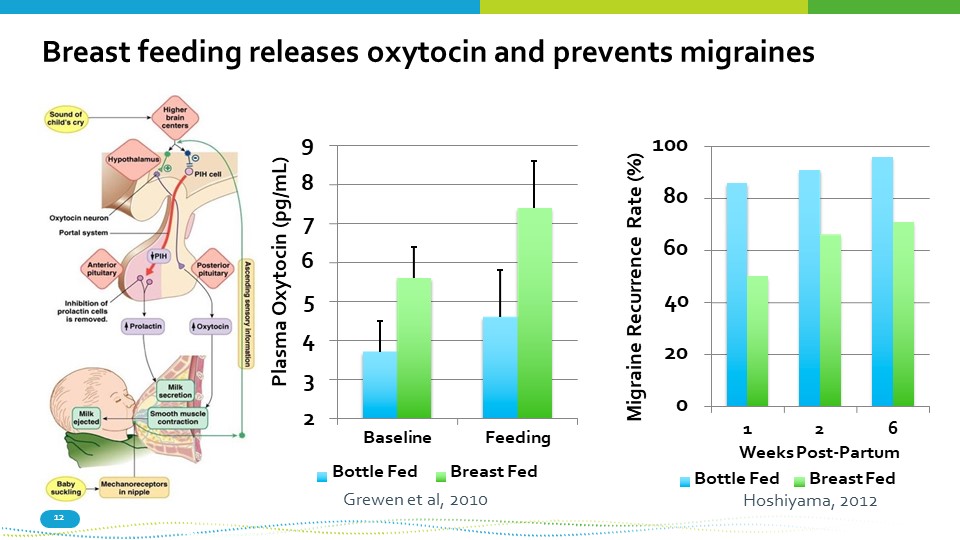
Breast feeding releases oxytocin and prevents migraines 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Baseline Bottle Fed Feeding Breast Fed Plasma Oxytocin (pg/mL) 0 20 40 60 80 100 1 2 6 Weeks Post - Partum Migraine Recurrence Rate (%) Grewen et al, 2010 12 Bottle Fed Breast Fed Hoshiyama, 2012
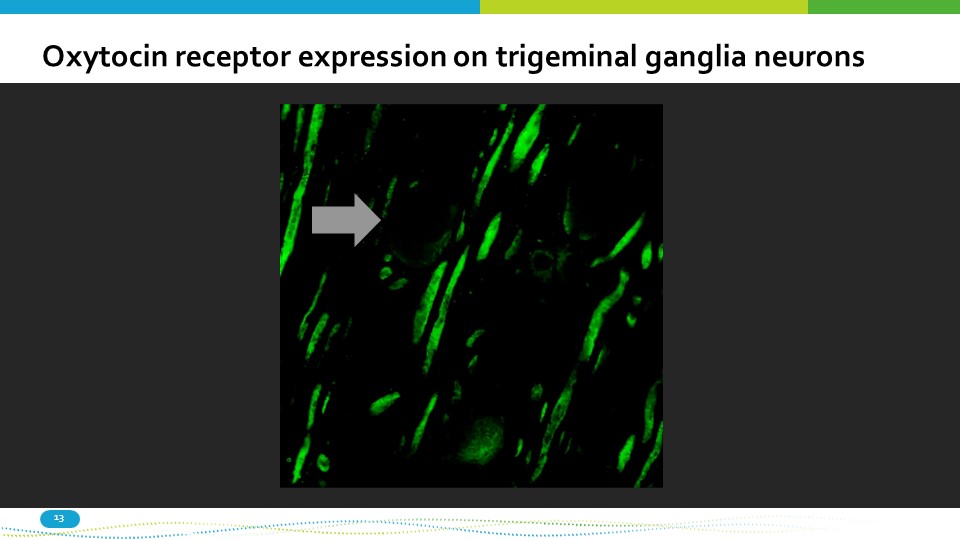
Oxytocin receptor expression on trigeminal ganglia neurons 13
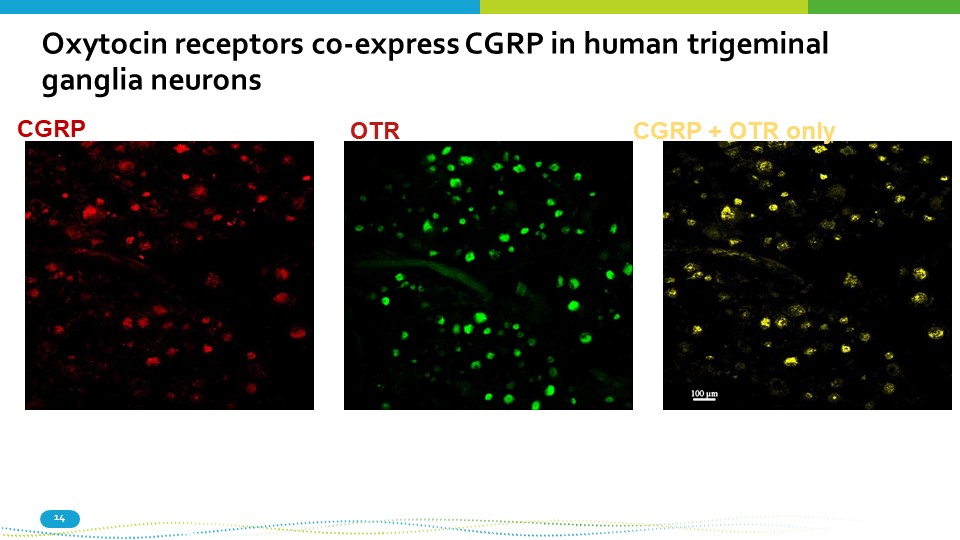
CGRP 14 OTR CGRP + OTR only Oxytocin receptors co - express CGRP in human trigeminal ganglia neurons
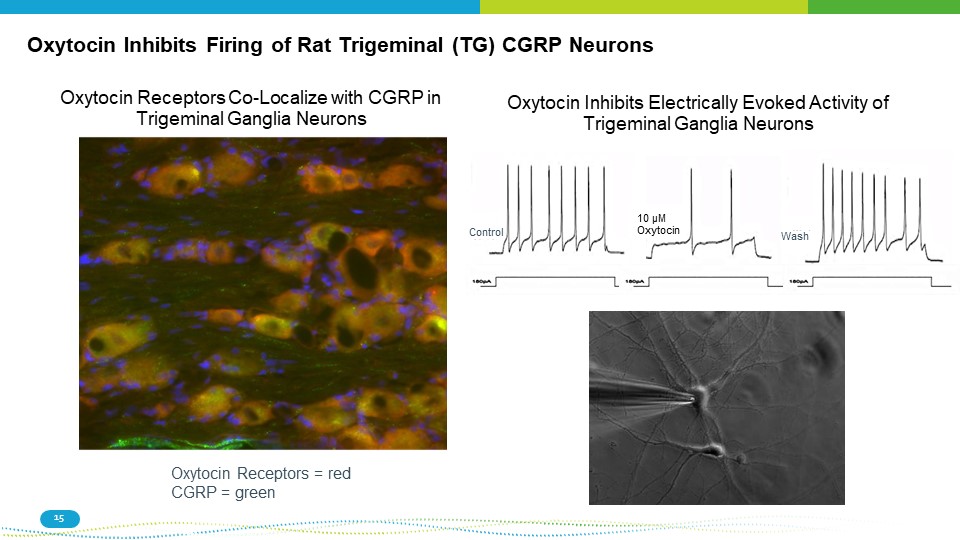
Oxytocin Inhibits Firing of Rat Trigeminal (TG) CGRP Neurons Oxytocin Receptors Co - Localize with CGRP in Trigeminal Ganglia Neurons Oxytocin Receptors = red CGRP = green Oxytocin Inhibits Electrically Evoked Activity of Trigeminal Ganglia Neurons 10 μM Oxytocin Control Wash 15
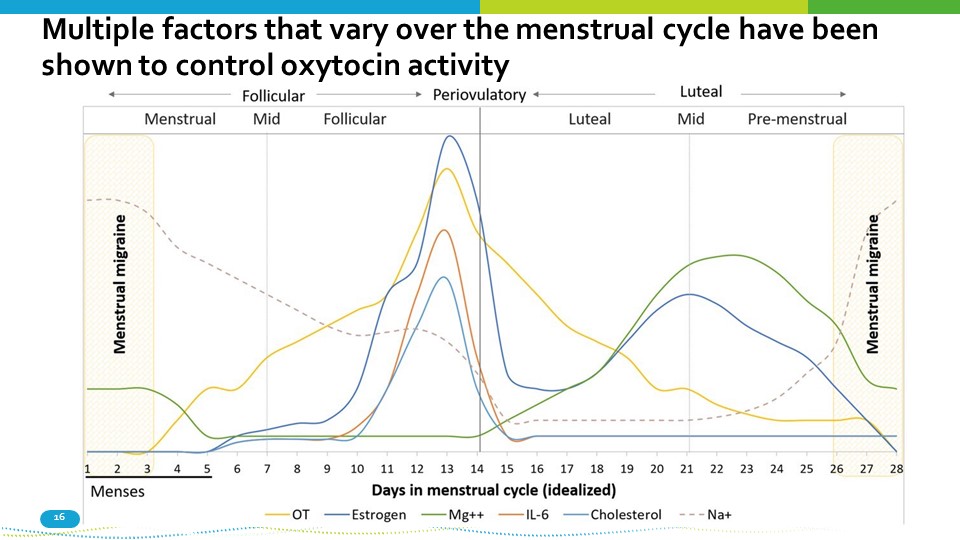
Multiple factors that vary over the menstrual cycle have been shown to control oxytocin activity 16
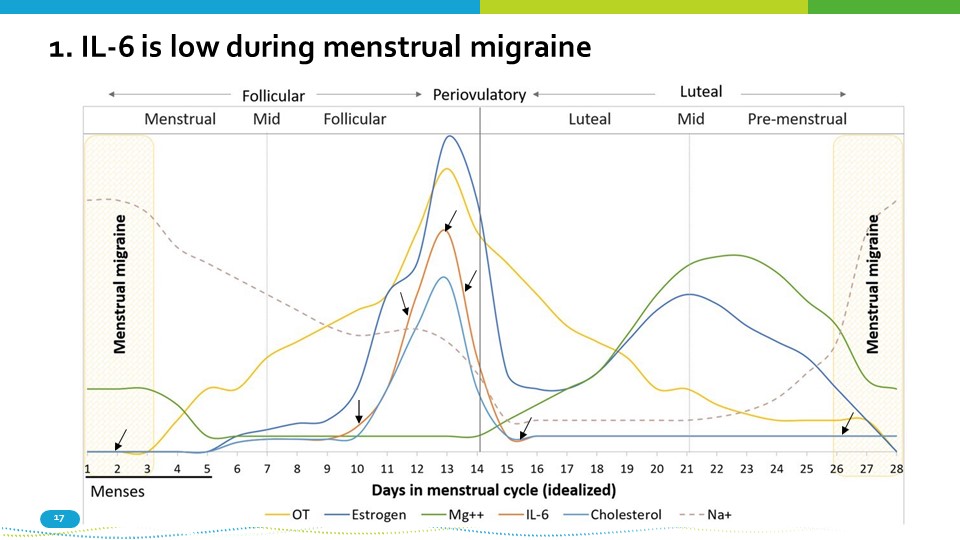
1. IL - 6 is low during menstrual migraine 17
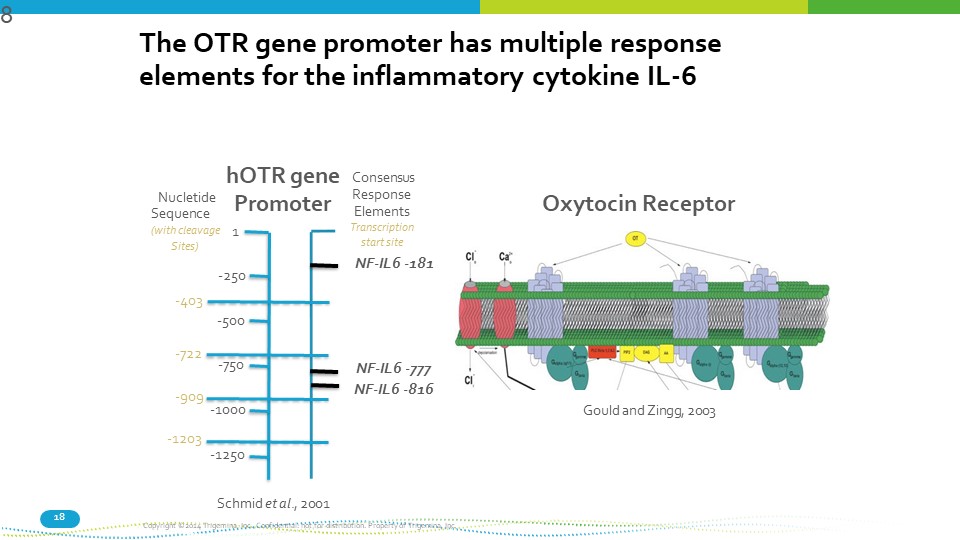
18 The OTR gene promoter has multiple response elements for the inflammatory cytokine IL - 6 Nucletide Sequence (with cleavage Sites) 1 - 250 - 750 - 1000 - 403 - 500 - 722 - 909 - 1203 - 1250 hOTR gene Promoter Consensus Response Elements Transcription start site NF - IL6 - 181 NF - IL6 - 777 NF - IL6 - 816 Oxytocin Receptor Schmid et al ., 2001 Copyright ©2014 Trigemina, Inc. Confidential: not for distribution. Property of Trigemina, Inc. Gould and Zingg, 2003 8
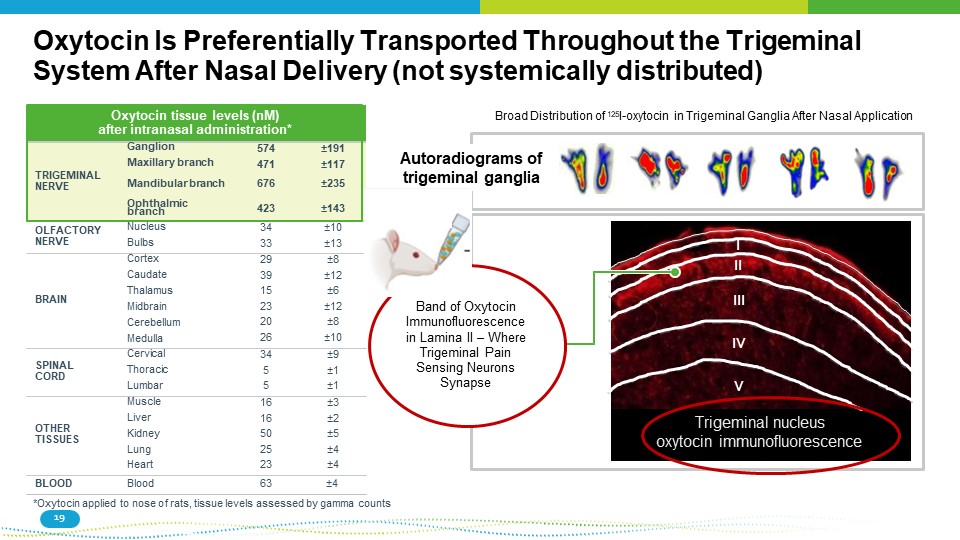
Trigeminal nucleus oxytocin immunofluorescence I II III IV V Autoradiograms of trigeminal ganglia Oxytocin Is Preferentially Transported Throughout the Trigeminal System After Nasal Delivery (not systemically distributed) Oxytocin tissue levels (nM) after intranasal administration* TRIGEMINAL NERVE Ganglion Maxillary branch Mandibular branch 574 471 676 “ 191 “ 117 “ 235 Ophthalmic branch 423 “ 143 OLFACTORY NERVE Nucleus Bulbs 34 33 “ 10 “ 13 BRAIN Cortex Caudate Thalamus Midbrain Cerebellum Medulla 29 39 15 23 20 26 “ 8 “ 12 “ 6 “ 12 “ 8 “ 10 SPINAL CORD Cervical Thoracic Lumbar 34 5 5 “ 9 “ 1 “ 1 OTHER TISSUES Muscle Liver Kidney Lung Heart 16 16 50 25 23 “ 3 “ 2 “ 5 “ 4 “ 4 BLOOD Blood 63 “ 4 *Oxytocin applied to nose of rats, tissue levels assessed by gamma counts Broad Distribution of 125 I - oxytocin in Trigeminal Ganglia After Nasal Application Band of Oxytocin Immunofluorescence in Lamina II – Where Trigeminal Pain Sensing Neurons Synapse 19
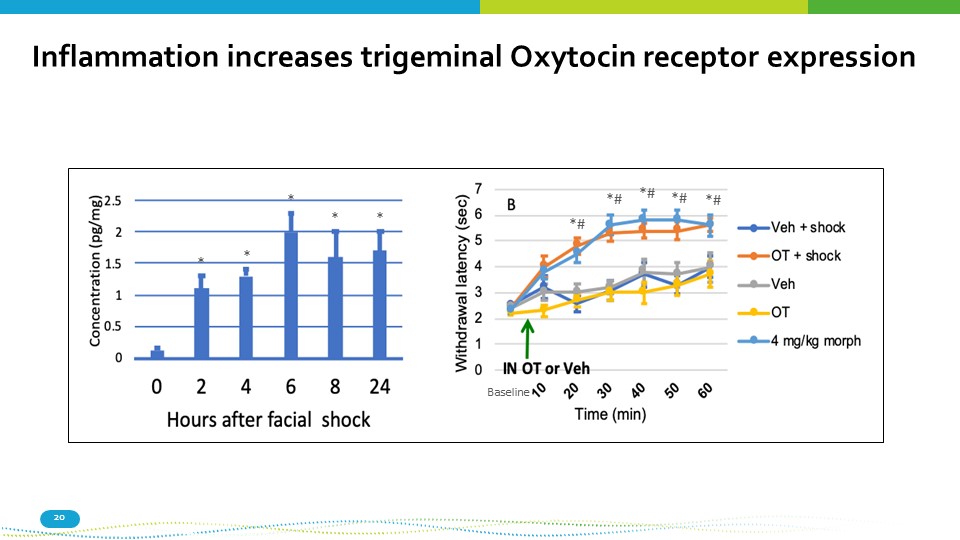
Inflammation increases trigeminal Oxytocin receptor expression *# *# *# *# *# * * * * * Baseline 20
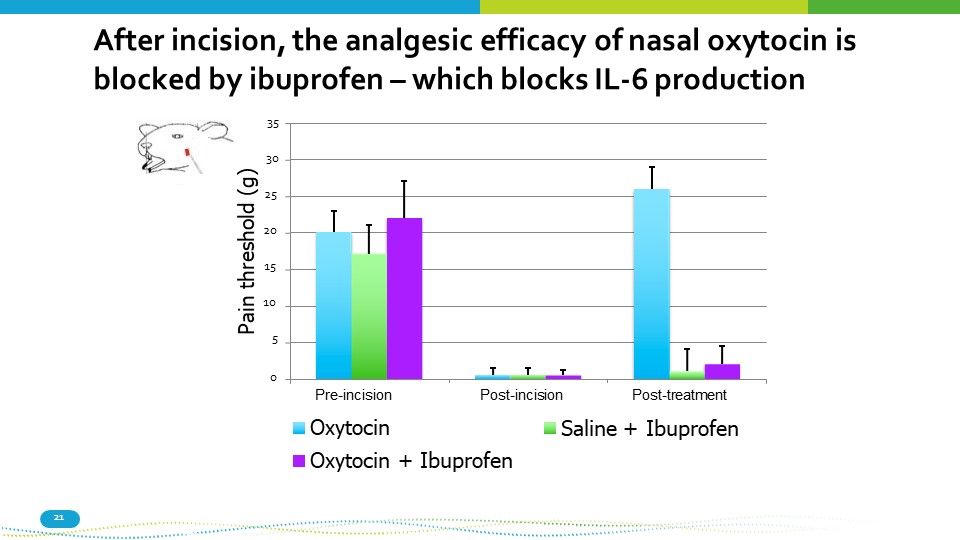
0 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 1 2 3 Pain threshold (g) Saline + Ibuprofen After incision, the analgesic efficacy of nasal oxytocin is blocked by ibuprofen – which blocks IL - 6 production Pre - incision Post - incision Oxytocin Oxytocin + Ibuprofen 21 Post - treatment
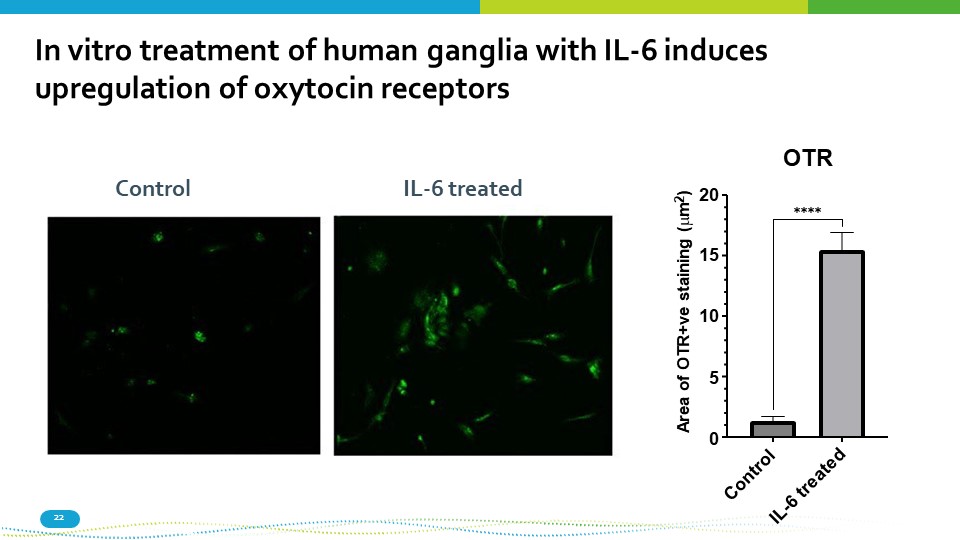
15 10 5 0 20 OTR Area of OTR+ve staining ( m 2 ) ٓٓٓٓ In vitro treatment of human ganglia with IL - 6 induces upregulation of oxytocin receptors Control 22 IL - 6 treated
Nasal delivery of oxytocin to the trigeminal system of humans 23
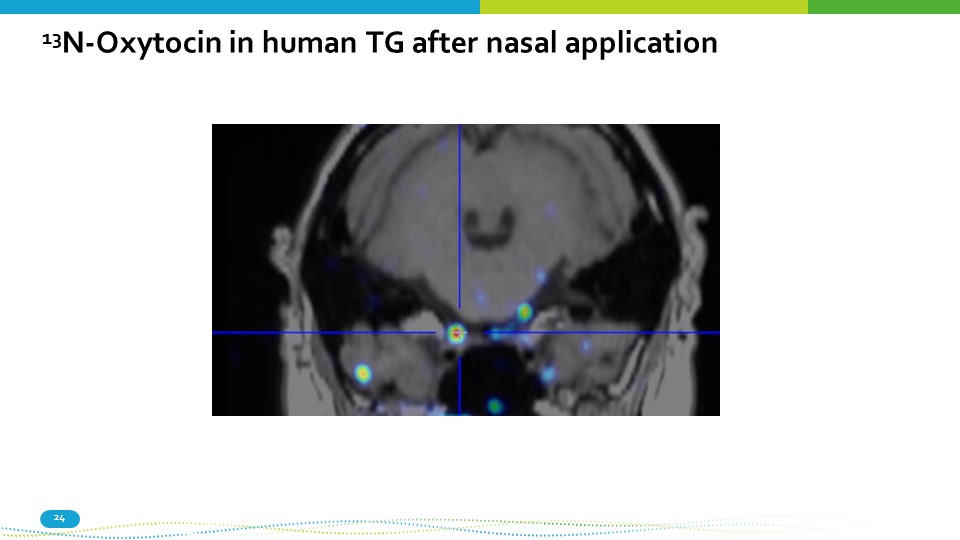
13 N - Oxytocin in human TG after nasal application 24
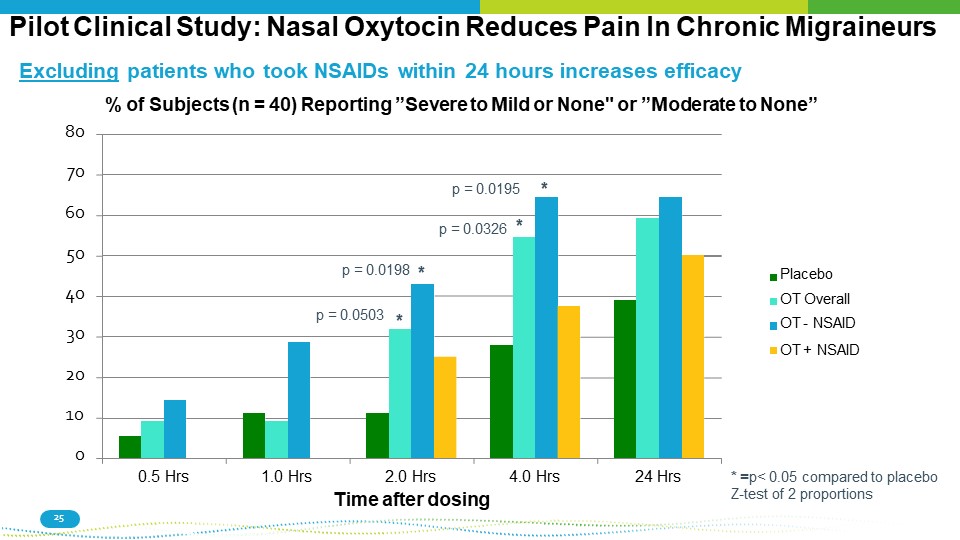
Pilot Clinical Study: Nasal Oxytocin Reduces Pain In Chronic Migraineurs * = p< 0.05 compared to placebo Z - test of 2 proportions 20 10 0 30 40 50 60 0.5 Hrs 1.0 Hrs 2.0 Hrs Time after dosing 4.0 Hrs 24 Hrs Placebo OT Overall OT - NSAID OT + NSAID * 25 p = 0.0195 p = 0.0326 * * p = 0.0503 p = 0.0198 * Excluding patients who took NSAIDs within 24 hours increases efficacy % of Subjects (n = 40) Reporting ”Severe to Mild or None" or ”Moderate to None” 80 70
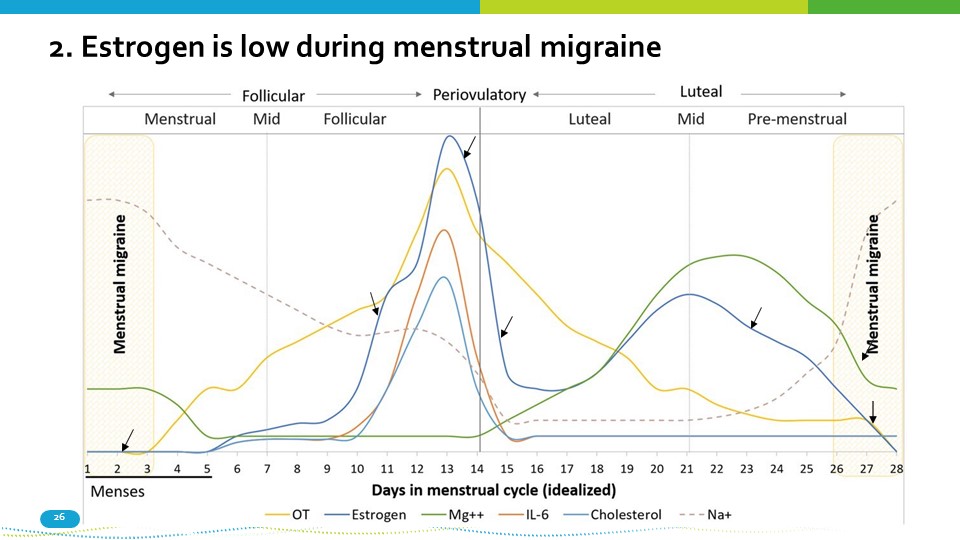
2. Estrogen is low during menstrual migraine 26
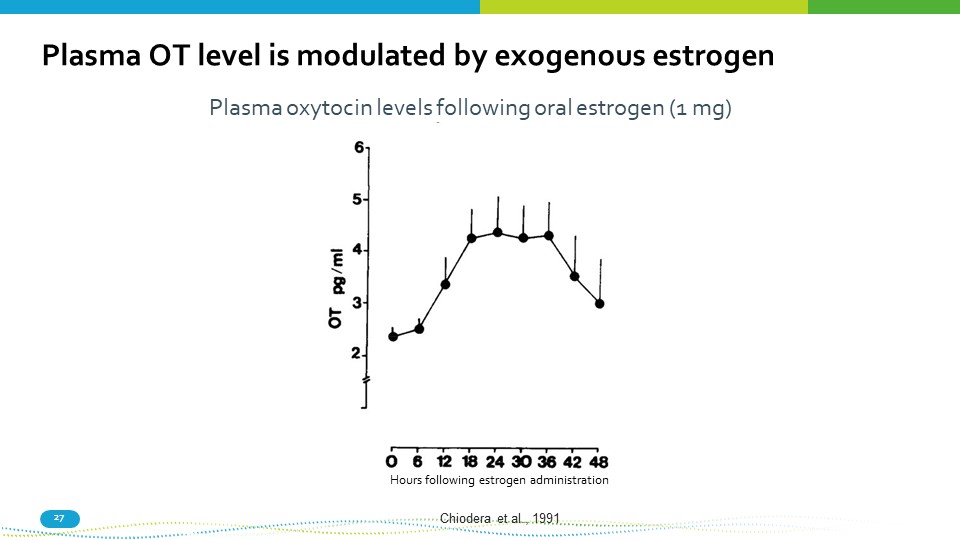
27 Plasma OT level is modulated by exogenous estrogen Chiodera et al., 1991 Plasma oxytocin levels following oral estrogen (1 mg) Hours following estrogen administration
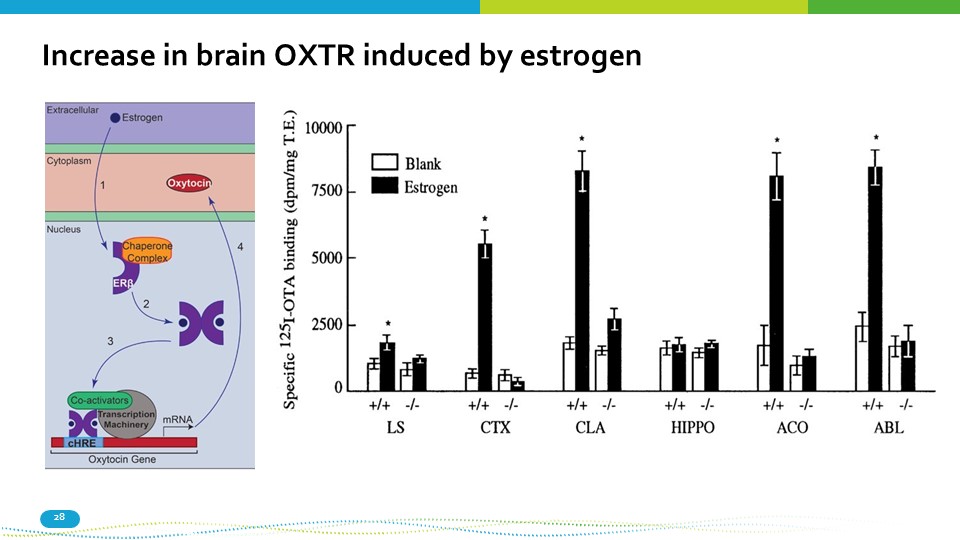
Increase in brain OXTR induced by estrogen 28
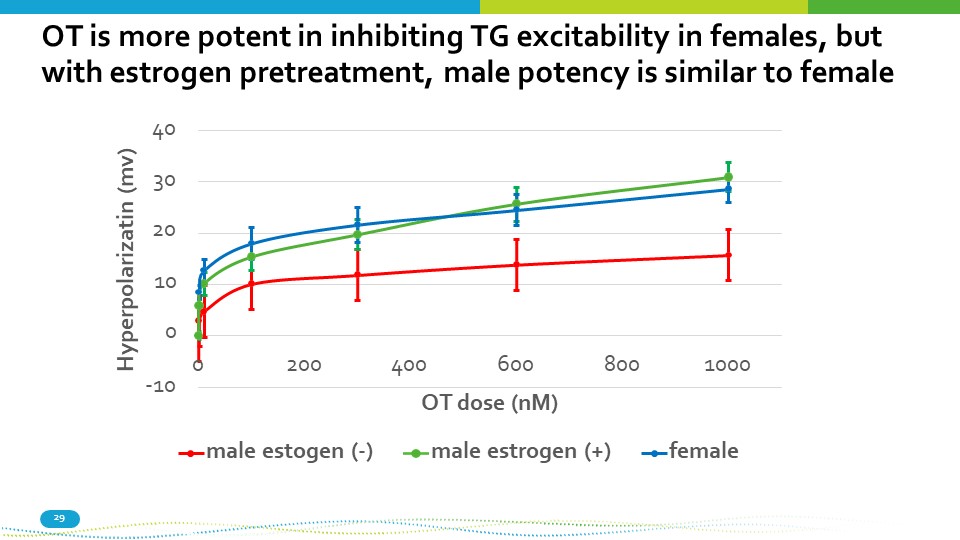
OT is more potent in inhibiting TG excitability in females, but with estrogen pretreatment, male potency is similar to female - 10 40 30 20 10 0 0 200 800 1000 400 600 OT dose (nM) Hyperpolarizatin (mv) male estogen ( - ) male estrogen (+) female 29
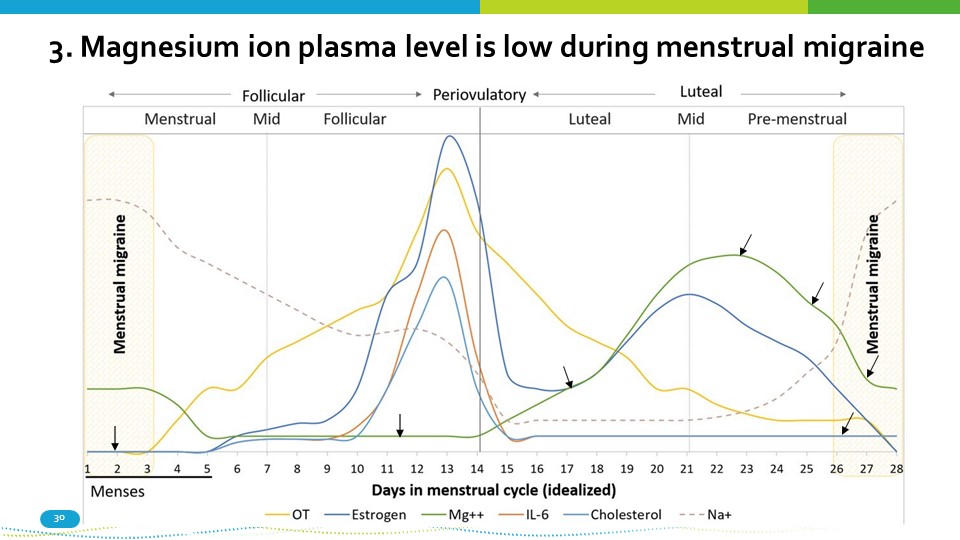
3. Magnesium ion plasma level is low during menstrual migraine 30
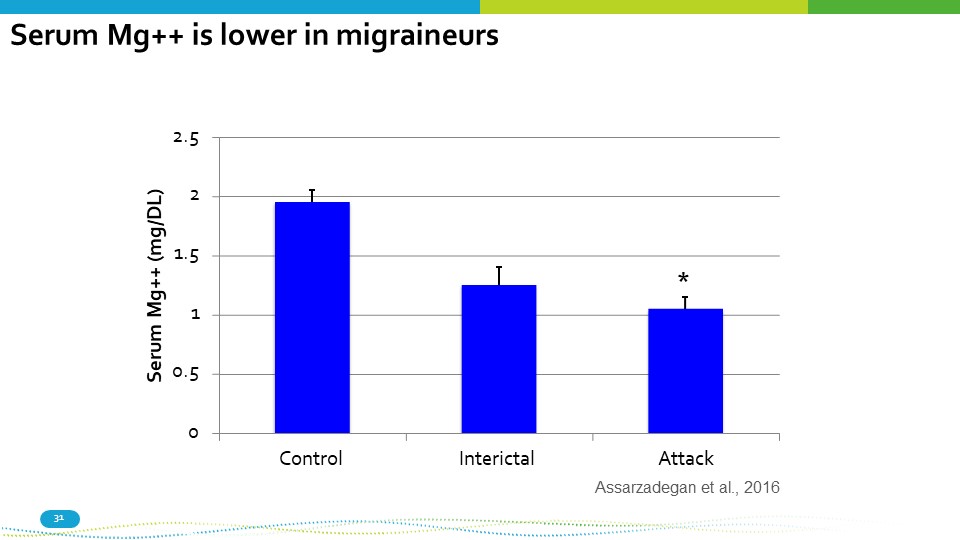
Attack Assarzadegan et al., 2016 31 0 1 0.5 2.5 2 1.5 Control Interictal Serum Mg++ (mg/DL) * Serum Mg++ is lower in migraineurs
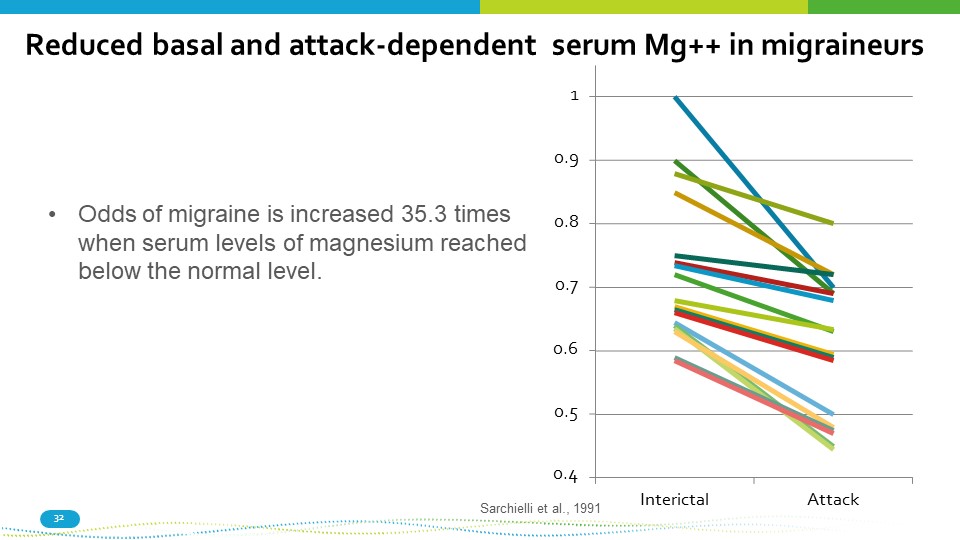
Reduced basal and attack - dependent serum Mg++ in migraineurs Sarchielli et al., 1991 0.6 0.5 0.4 32 0.7 0.8 1 0.9 Interictal Attack • Odds of migraine is increased 35.3 times when serum levels of magnesium reached below the normal level.
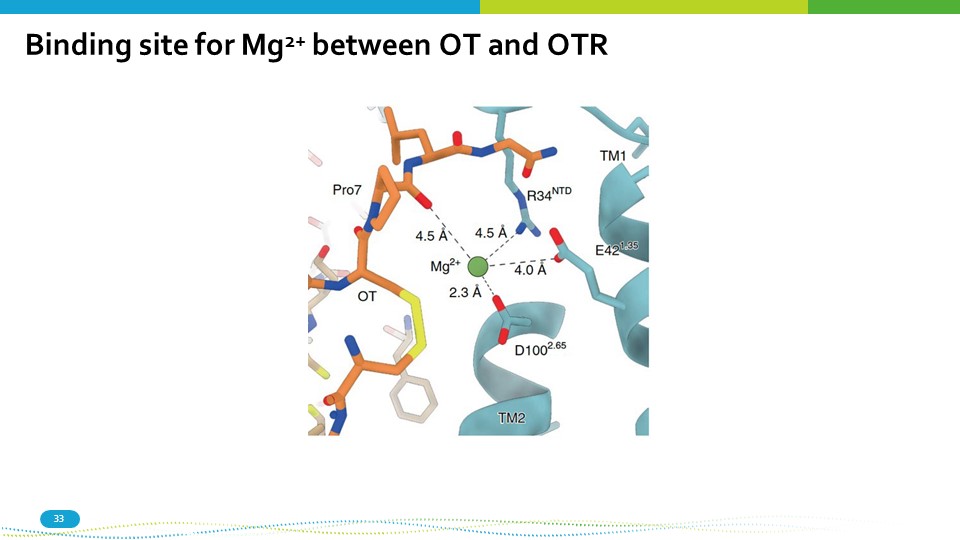
Binding site for Mg 2+ between OT and OTR 33
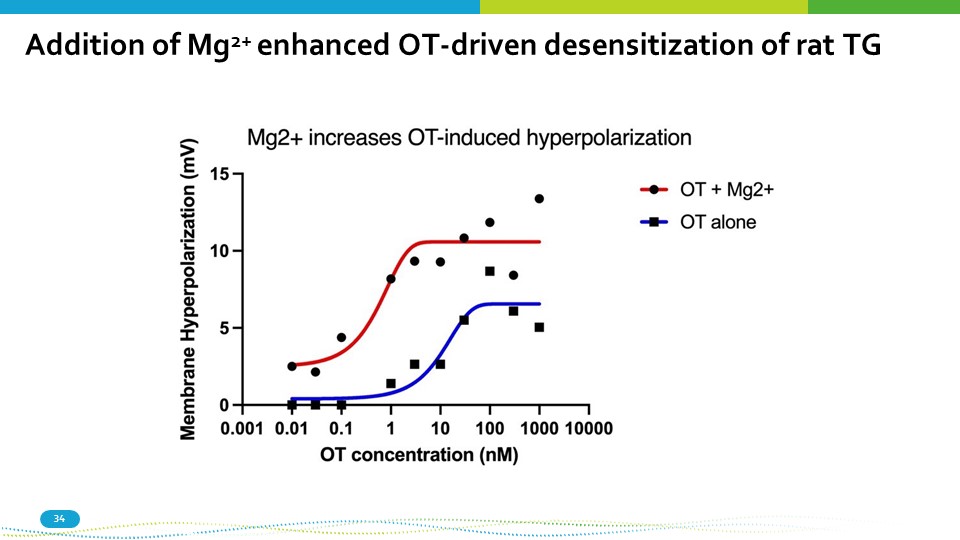
Addition of Mg 2+ enhanced OT - driven desensitization of rat TG 34
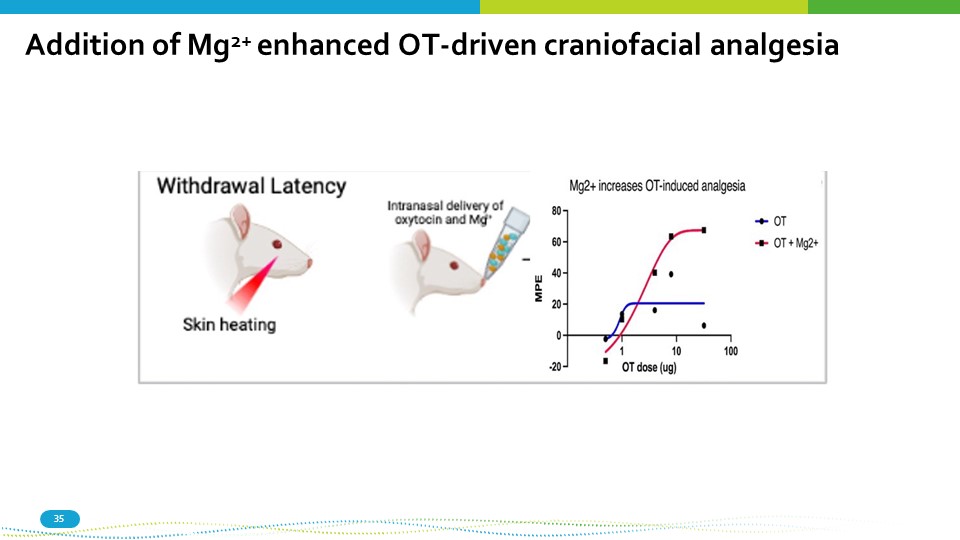
Addition of Mg 2+ enhanced OT - driven craniofacial analgesia 35
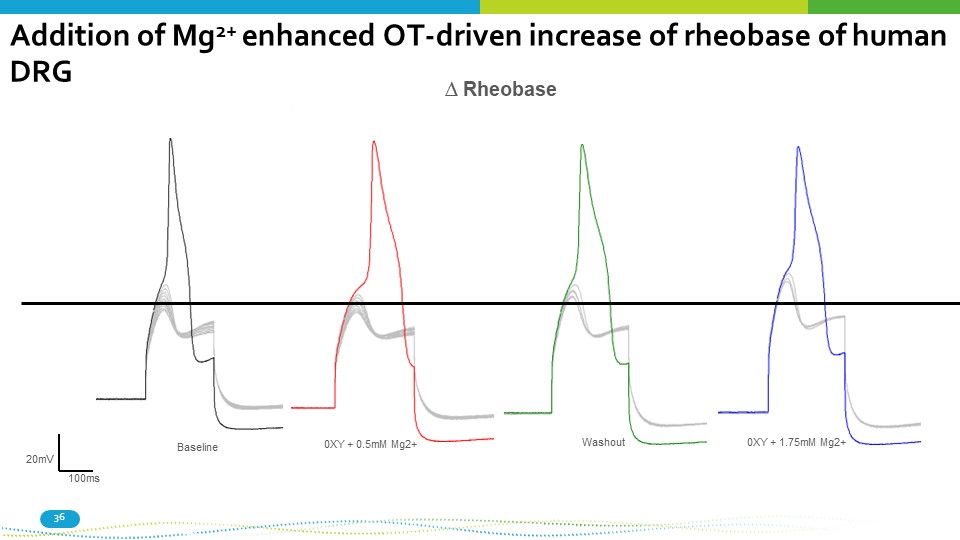
0XY + 0.5mM Mg2+ 0XY + 1.75mM Mg2+ Washout Baseline 20mV 100ms ∆ Rheobase Addition of Mg 2+ enhanced OT - driven increase of rheobase of human 36 DRG
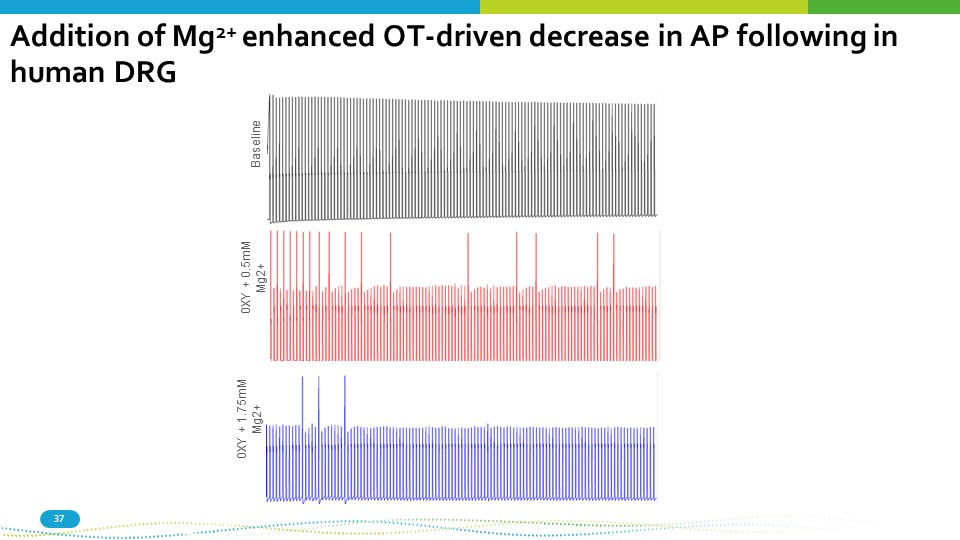
Baseline 37 0XY + 0.5mM Mg2+ 0XY + 1.75mM Mg2+ Addition of Mg 2+ enhanced OT - driven decrease in AP following in human DRG
Summary: Sex hormone modulation of migraine 38 • Evidence for Direct modulation of TG excitability by primary sex hormones in not strong • Evidence for extended sex hormones (Prolactin, oxytocin) robust • Oxytocin effects are modulated by several endogenous factors that vary over the menstrual cycle • IL - 6 levels drive OT receptor expression and increases OT analgesic efficacy • Estrogen drives OT and OT receptor expression and likely enables OT analgesia • Mg 2+ is decreased during menstruation and during migraine attacks • There is a binding site for Mg 2+ between OT and its receptor • Mg 2+ dramatically increases the analgesic efficacy of OT in animal models and human sensory neurons A Mg 2+ containing nasal formulation of OT is being used in an ongoing multi - site US study of chronic migraine prophylaxis

Alternatively, hugging, massage, sex, looking at your dog could help prevent migraines 39

Thank you! 40