Exhibit 99.1

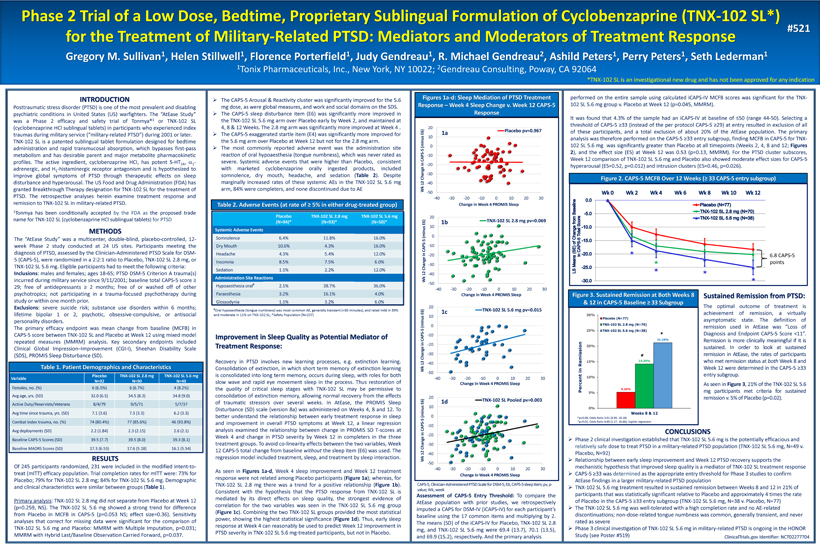
Phase 2 Trial of a Low Dose, Bedtime, Proprietary Sublingual Formulation of Cyclobenzaprine (TNX - 102 SL*) for the Treatment of Military - Related PTSD: Mediators and Moderators of Treatment Response Gregory M. Sullivan 1 , Helen Stillwell 1 , Florence Porterfield 1 , Judy Gendreau 1 , R. Michael Gendreau 2 , Ashild Peters 1 , Perry Peters 1 , Seth Lederman 1 1 Tonix Pharmaceuticals, Inc., New York, NY 10022; 2 Gendreau Consulting, Poway, CA 92064 INTRODUCTION Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is one of the most prevalent and disabling psychiatric conditions in United States (US) warfighters . The “AtEase Study” was a Phase 2 efficacy and safety trial of Tonmya® 1 or TNX - 102 SL (cyclobenzaprine HCl sublingual tablets) in participants who experienced index traumas during military service (“military - related PTSD”) during 2001 or later . TNX - 102 SL is a patented sublingual tablet formulation designed for bedtime administration and rapid transmucosal absorption, which bypasses first - pass metabolism and has desirable parent and major metabolite pharmacokinetic profiles . The active ingredient, cyclobenzaprine HCI, has potent 5 - HT 2 A , a 1 - adrenergic, and H 1 - histaminergic receptor antagonism and is hypothesized to improve global symptoms of PTSD through therapeutic effects on sleep disturbance and hyperarousal . The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Breakthrough Therapy designation for TNX - 102 SL for the treatment of PTSD . The retrospective analyses herein examine treatment response and remission to TNX - 102 SL in military - related PTSD . 1 Tonmya has been conditionally accepted by the FDA as the proposed trade name for TNX - 102 SL (cyclobenzaprine HCl sublingual tablets ) for PTSD METHODS The “AtEase Study” was a multicenter, double - blind, placebo - controlled, 12 - week Phase 2 study conducted at 24 US sites . Participants meeting the diagnosis of PTSD, assessed by the Clinician - Administered PTSD Scale for DSM - 5 (CAPS - 5 ), were randomized in a 2 : 2 : 1 ratio to Placebo, TNX - 102 SL 2 . 8 mg, or TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg . Eligible participants had to meet the following criteria : Inclusions : males and females ; ages 18 - 65 ; PTSD DSM - 5 Criterion A trauma(s) incurred during military service since 9 / 11 / 2001 ; baseline total CAPS - 5 score ≥ 29 ; free of antidepressants ≥ 2 months ; free of or washed off of other psychotropics ; not participating in a trauma - focused psychotherapy during study or within one month prior . Exclusions : severe suicide risk ; substance use disorders within 6 months ; lifetime bipolar 1 or 2 , psychotic, obsessive - compulsive, or antisocial personality disorders . The primary efficacy endpoint was mean change from baseline (MCFB) in CAPS - 5 score between TNX - 102 SL and Placebo at Week 12 using mixed model repeated measures (MMRM) analysis . Key secondary endpoints included Clinical Global Impression – Improvement (CGI - I), Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS), PROMIS Sleep Disturbance (SD) . ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02277704 #521 *TNX - 102 SL is an investigational new drug and has not been approved for any indication Table 1. Patient Demographics and Characteristics Variable Placebo N=92 TNX - 102 SL 2.8 mg N=90 TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg N=49 Females, no. (%) 6 (6.5%) 6 (6.7%) 4 (8.2%) Avg age, yrs. (SD) 32.0 (6.5) 34.5 (8.3) 34.8 (9.0) A ctive Duty /R eservists/Veterans 8/4/79 9/5/71 5/7/37 Avg time since trauma, yrs. (SD) 7.1 (3.6) 7.3 (3.3) 6.2 (3.3) Combat index trauma, no. (%) 74 (80.4%) 77 (85.6%) 46 (93.8%) Avg deployments (SD) 2.2 (1.84) 2.3 (2.15) 2.6 (2.1) Baseline CAPS - 5 Scores (SD) 39.5 (7.7) 39.5 (8.0) 39.3 (8.1) Baseline MADRS Scores (SD) 17.3 (6.53) 17.6 (5.18) 16.1 (5.54) » The CAPS - 5 Arousal & Reactivity cluster was significantly improved for the 5 . 6 mg dose, as were global measures, and work and social domains on the SDS . » The CAPS - 5 sleep disturbance item (E 6 ) was significantly more improved in the TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg arm over Placebo early by Week 2 , and maintained at 4 , 8 & 12 Weeks . The 2 . 8 mg arm was significantly more improved at Week 4 . » The CAPS - 5 exaggerated startle item (E 4 ) was significantly more improved for the 5 . 6 mg arm over Placebo at Week 12 but not for the 2 . 8 mg arm . » The most commonly reported adverse event was the administration site reaction of oral hypoaesthesia (tongue numbness), which was never rated as severe . Systemic adverse events that were higher than Placebo, consistent with marketed cyclobenzaprine orally ingested products, included somnolence, dry mouth, headache, and sedation ( Table 2 ) . Despite marginally increased rates of these systemic AEs in the TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg arm, 84 % were completers, and none discontinued due to AE Placebo (N=94)* TNX - 102 SL 2.8 mg (N=93)* TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg (N=50)* Systemic Adverse Events Somnolence 6.4% 11.8% 16.0% Dry Mouth 10.6% 4.3% 16.0% Headache 4.3% 5.4% 12.0% Insomnia 8.5% 7.5% 6.0% Sedation 1.1% 2.2% 12.0% Administration Site Reactions Hypoaesthesia oral # 2.1% 38.7% 36.0% Paraesthesia 3.2% 16.1% 4.0% Glossodynia 1.1% 3.2% 6.0% # Oral hypoaesthesia (tongue numbness) was most common AE, generally transient (<60 minutes), and rated mild in 89% and moderate in 11% on TNX - 102 SL; *Safety Population (N=237) Table 2. Adverse Events (at rate of ≥ 5% in either drug - treated group) Assessment of CAPS - 5 Entry Threshold : To compare the AtEase population with prior studies, we retrospectively imputed a CAPS for DSM - IV (iCAPS - IV) for each participant’s baseline using the 17 common items and multiplying by 2 . The means (SD) of the iCAPS - IV for Placebo, TNX - 102 SL 2 . 8 mg, and TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg were 69 . 4 ( 13 . 7 ), 70 . 1 ( 13 . 5 ), and 69 . 9 ( 15 . 2 ), respectively . And the primary analysis -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 Wk 12 Change in CAPS - 5 (minus E6) Change in Week 4 PROMIS Sleep Placebo pv=0.967 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 Wk 12 Change in CAPS - 5 (minus E6) Change in Week 4 PROMIS Sleep TNX-102 SL 5.6 mg pv=0.015 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 Wk 12 Change in CAPS - 5 (minus E6) Change in Week 4 PROMIS Sleep TNX-102 SL 2.8 mg pv=0.069 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 Wk 12 Change in CAPS - 5 (minus E6) Change in Week 4 PROMIS Sleep TNX-102 SL Pooled pv=0.003 CAPS - 5, Clinician - Administered PTSD Scale for DSM - 5; E6, CAPS - 5 sleep item; pv, p - value; Wk, week Sustained Remission from PTSD : The optimal outcome of treatment is achievement of remission, a virtually asymptomatic state . The definition of remission used in AtEase was “Loss of Diagnosis and Endpoint CAPS - 5 Score < 11 ” . Remission is more clinically meaningful if it is sustained . In order to look at sustained remission in AtEase, the rates of participants who met remission status at both Week 8 and Week 12 were determined in the CAPS - 5 ≥ 33 entry subgroup . As seen in Figure 3 , 21 % of the TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg participants met criteria for sustained remission v . 5 % of Placebo (p= 0 . 02 ) . Improvement in Sleep Quality as Potential Mediator of Treatment Response: Recovery in PTSD involves new learning processes, e . g . extinction learning . Consolidation of extinction, in which short term memory of extinction learning is consolidated into long term memory, occurs during sleep, with roles for both slow wave and rapid eye movement sleep in the process . Thus r estoration of the quality of critical sleep stages with TNX - 102 SL may be permissive to consolidation of extinction memory, allowing normal recovery from the effects of traumatic stressors over several weeks . In AtEase, the PROMIS Sleep Disturbance (SD) scale (version 8 a) was administered on Weeks 4 , 8 and 12 . To better understand the relationship between early treatment response in sleep and improvement in overall PTSD symptoms at Week 12 , a linear regression analysis examined the relationship between change in PROMIS SD T - scores at Week 4 and change in PTSD severity by Week 12 in completers in the three treatment groups . To avoid co - linearity effects between the two variables, Week 12 CAPS - 5 total change from baseline without the sleep item (E 6 ) was used . The regression model included treatment, sleep, and treatment by sleep interaction . As seen in Figures 1 a - d , Week 4 sleep improvement and Week 12 treatment response were not related among Placebo participants ( Figure 1 a ) ; whereas, for TNX - 102 SL 2 . 8 mg there was a trend for a positive relationship ( Figure 1 b ) . Consistent with the hypothesis that the PTSD response from TNX - 102 SL is mediated by its direct effects on sleep quality, the strongest evidence of correlation for the two variables was seen in the TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg group ( Figure 1 c ) . Combining the two TNX - 102 SL groups provided the most statistical power, showing the highest statistical significance ( Figure 1 d ) . Thus, early sleep response at Week 4 can reasonably be used to predict Week 12 improvement in PTSD severity in TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg - treated participants, but not in Placebo . # p=0.08, Odds Ratio 3.01 (0.89, 10.18) *p=0.02, Odds Ratio 4.60 (1.27, 16.66); logistic regression CONCLUSIONS » Phase 2 clinical investigation established that TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg is the potentially efficacious and relatively safe dose to treat PTSD in a military - related PTSD population (TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg, N=49 v. Placebo, N=92) » Relationship between early sleep improvement and Week 12 PTSD recovery supports the mechanistic hypothesis that improved sleep quality is a mediator of TNX - 102 SL treatment response » CAPS - 5 ≥33 was determined as the appropriate entry threshold for Phase 3 studies to confirm AtEase findings in a larger military - related PTSD population » TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg treatment resulted in sustained remission between Weeks 8 and 12 in 21% of participants that was statistically significant relative to Placebo and approximately 4 times the rate of Placebo in the CAPS - 5 ≥33 entry subgroup (TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg, N=38 v. Placebo, N=77) » The TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg was well - tolerated with a high completion rate and no AE - related discontinuations; non - dose - related tongue numbness was common, generally transient, and never rated as severe » Phase 3 clinical investigation of TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg in military - related PTSD is ongoing in the HONOR Study ( see Poster #519) Figures 1a - d: Sleep Mediation of PTSD Treatment Response – Week 4 Sleep Change v. Week 12 CAPS - 5 Response Figure 2. CAPS - 5 MCFB Over 12 Weeks ( ≥ 33 CAPS - 5 entry subgroup) Figure 3. Sustained Remission at Both Weeks 8 & 12 in CAPS - 5 Baseline ≥ 33 Subgroup performed on the entire sample using calculated iCAPS - IV MCFB scores was significant for the TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg group v . Placebo at Week 12 (p= 0 . 045 , MMRM) . It was found that 4 . 3 % of the sample had an iCAPS - IV at baseline of ≤ 50 (range 44 - 50 ) . Selecting a threshold of CAPS - 5 ≥ 33 (instead of the per protocol CAPS - 5 ≥ 29 ) at entry resulted in exclusion of all of these participants, and a total exclusion of about 20 % of the AtEase population . The primary analysis was therefore performed on the CAPS - 5 ≥ 33 entry subgroup , finding MCFB in CAPS - 5 for TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg was significantly greater than Placebo at all timepoints (Weeks 2 , 4 , 8 and 12 ; Figures 2 ), and the effect size (ES) at Week 12 was 0 . 53 (p= 0 . 13 , MMRM) . For the PTSD cluster subscores, Week 12 comparison of TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg and Placebo also showed moderate effect sizes for CAPS - 5 hyperarousal (ES= 0 . 52 , p= 0 . 012 ) and intrusion clusters (ES= 0 . 46 , p= 0 . 026 ) . * * * * * 6.8 CAPS - 5 points RESULTS Of 245 participants randomized, 231 were included in the modified intent - to - treat (mITT) efficacy population . Trial completion rates for mITT were : 73 % for Placebo ; 79 % for TNX - 102 SL 2 . 8 mg ; 84 % for TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg . Demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between groups ( Table 1 ) . Primary analysis : TNX - 102 SL 2 . 8 mg did not separate from Placebo at Week 12 (p= 0 . 259 , NS) . The TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg showed a strong trend for difference from Placebo in MCFB in CAPS - 5 (p= 0 . 053 NS ; effect size= 0 . 36 ) . Sensitivity analyses that correct for missing data were significant for the comparison of TNX - 102 SL 5 . 6 mg and Placebo : MMRM with Multiple Imputation, p= 0 . 031 ; MMRM with Hybrid Last/Baseline Observation Carried Forward, p= 0 . 037 . 1a 1b 1c 1d Presented at the Military Health System Research Symposium (MHSRS) in Kissimmee, FL August 27 - 30; MHSRS - 17 - 1685 Poster Session 2 – Poster #521, 10:00 AM – 4:30 PM EDT, Florida Exhibit Hall D - F