
Exhibit 99.01

1 An AFSP/ASCP Workshop: Inclusion of Suicidal Individuals in Treatment Trials: Now is the Time Wed May 30 th 2:45 - 4:45PM Poinciana 1 - 2 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Including Suicidal Individuals in Treatment Trials: Treatment of Military - Related PTSD with TNX - 102 SL, a Novel Sublingual Formulation of Cyclobenzaprine Hypothesized to Address PTSD through Improvement in Sleep Quality Gregory Sullivan MD Chief Medical Officer Tonix Pharmaceuticals

2 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Disclosures • Gregory Sullivan MD is an employee of Tonix Pharmaceuticals and owns stock and stock options in the company • TNX - 102 SL is an investigational new drug and has not been approved for any indication • Presentation contains mention of two off - label uses of medications (lithium for reducing suicidal behaviors in bipolar disorder and ketamine for reducing suicidal behaviors in major depressive disorder)

3 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Including Suicidal Individuals in Clinical Trials • Multiple psychiatric disorders are associated with increased risk of suicide • Examples: Major Depression, Bipolar Disorder, Schizophrenia, PTSD • Making an impact on these suicide rates requires inclusion of this subpopulation in clinical trials • Focusing on patient safety, outpatient trials require some degree of exclusion of those at most imminent risk who likely need more comprehensive and possibly inpatient care • We have struck this balance in our Phase 2 trial of TNX - 102 SL for military - related PTSD and this is what we have learned
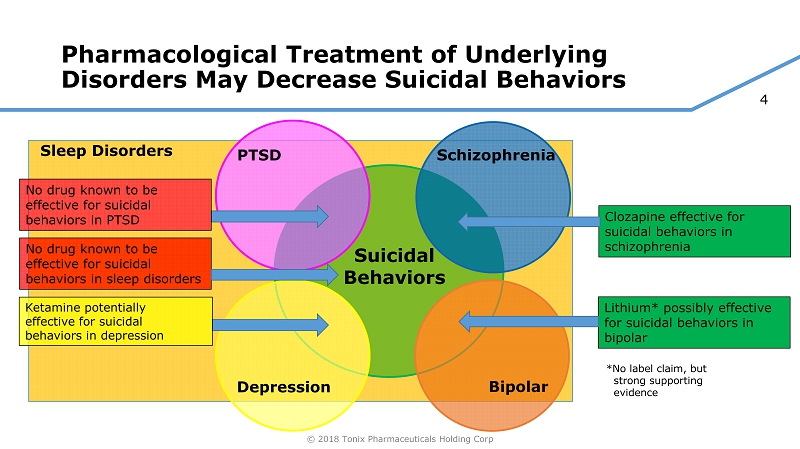
4 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Pharmacological Treatment of Underlying Disorders May Decrease Suicidal Behaviors Suicidal Behaviors PTSD Depression Schizophrenia Bipolar Clozapine effective for suicidal behaviors in schizophrenia Lithium* p ossibly effective for suicidal behaviors in bipolar *No label claim, but strong supporting evidence Sleep Disorders No drug known to be effective for suicidal behaviors in PTSD Ketamine potentially effective for suicidal behaviors in depression No drug known to be effective for suicidal behaviors in sleep disorders

5 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Studying Predictors of Suicide • Limited body of work on death from suicide, in part explained by: • Suicides being relatively rare events at the population level • Difficulty in predicting who will die by suicide even in high risk samples • Necessity for data collected prior to death • Research on predictors of suicide such as suicidal ideation and suicide attempts helps fill this critical gap, although caution is warranted: • Major limitation: only ~15% of those surviving a suicide attempt eventually die by suicide • These predictors do not necessarily provide information about a direct relationship between a psychiatric disorder such as PTSD (or a symptom such as sleep disturbance) and death by suicide • Interventional clinical trials in psychiatric disorders offer an important opportunity to learn more about predictors of suicide • And without biomarkers specific for predicting suicide, suicidal ideation and behaviors are the most definitive endpoints to assess an intervention aimed at preventing suicide

6 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Suicide - PTSD Link Established but Controversy Remains Abundance of evidence suggests PTSD increases risk of death by suicide • Consistent evidence of a strong association while accounting for pre - existing psychiatric comorbidity 1 • Danish registry (n=208,918) study found 5.3 greater rate of death from suicide for persons with PTSD than without (adjusted for gender, age, marital status, income, pre - existing depression diagnosis) • Denmark study (n=22,716) found 13 times the rate with PTSD • US Army service members 2001 - 2009 who died by suicide almost 13 times more likely have received PTSD diagnosis compared to all Army service members for same time period • Picture somewhat clouded by several studies suggesting a protective effect of PTSD from death by suicide 1 • Some of these findings may be explained by methodological biases • In samples with high levels of “comorbid PTSD and depression”, statistical adjustment for depression may adjust out elements of PTSD, i.e. DSM - 5 PTSD cluster D symptoms, that are most related to suicide risk • If depression is on a causal pathway between PTSD and suicide (PTSD - >depression - >suicide), adjustment for depression would obscure the relationship • In studies with high levels of psychopathology, such as patients discharged from inpatient psychiatric units, risk of suicide from PTSD in comparison to reference groups with very elevated risk (e.g. MDD, bipolar disorder or schizophrenia) may look relatively protective 1 Gradus, PTSD Research Quarterly 2017 28:1 - 8.

7 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Suicides in the US Military • Suicide rate among active duty US Army personnel was increasing since 2004 1 • 2001: 9 per 100,000 • 2009: 22 per 100,000 • Surpassed comparable civilian rates in 2008 • Suicides in US military currently account for nearly 20% of all military deaths • Increase (2003 - 2008) paralleled by increase in prevalence of mental disorders across the Army • Rate of suicide for Active Component,* all Services: 2 19.9 per 100,000 • Most common methods: 2 • Firearms 68.3% • Hanging 24.9% • High risk and self - destructive behaviors also increased during the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, with substantial rise in motorcycle 3 and other motor vehicle deaths upon return to US 1 Black et al. Military Psychology 2011;23:433 - 451 2 Department of Defense Suicide Event Report ( DoDSER ), Cal Yr 2014 Ann Report 3 MSMR 2011;3:2 - 5. *Non - Reserve

8 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Rising Suicide Risk and Rates in US Veterans since 2001 • Retrospective multivariate analysis of 3.8 million US military personnel between 2001 - 2011 1 , with outcome of death by suicide in Cox proportional hazard models showed: • Hazard rate increased with first year of separation (HR 2.49) • Hazard rate remained elevated for those separated ≥ 6 years earlier (HR 1.63) • In 2014 2 ,18% of all suicides among US adults identified as veterans of the US military service • Since 2001 2 , the age - adjusted rate of suicide has increased among: • US veteran males by 30.5% • US veteran females by 85.2% 1 Shen et al, Lancet Psychiatry 2016;3:10 - 39 - 48. 2 VA Suicide Prevention Program, Facts about Veteran Suicide, July 2016

9 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Disturbed Sleep and Suicide Risk Abundance of evidence showing link between poor sleep and increased risk of suicidal ideation and behaviors • Large epidemiological studies showing sleep disturbance as risk for suicide death 1,2 • Specific sleep disturbance symptoms (i.e. insomnia and nightmares) have unique relationships with suicidal ideation, attempts, and suicide 3 • Suicidal ideation or attempts in individuals with PTSD criterion A - qualifying traumas higher among those with trauma - related nightmares (62%) than without (20%) 4 in prior month • Studies of veterans demonstrating link between insomnia and suicidal ideation 5,6,7 • Treatment study in v eterans showed reduced suicidal ideation among those receiving Cognitive Behavior Therapy for insomnia (N=405) 8 1 Bjorngaard et al. Sleep 2011 34:1155 - 9; 2 Fugino et al. Suicide Life Threat Behav 2005 35:227 - 37; 3 Pigeon et al. Sleep Med Clin 2015 10:41 - 8; 4 Littlewood et al. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2016 12:393 - 399; 5 Chkravorty et al. Addict Behav 2014 39:399 - 405; 6 Davidson et al. Suicide Life Threat Behav 2013 43:279 - 89; 7 Ribeiro et al. J Affect Disord 2012 136:743 - 50; 8 Trockel et al, Sleep 2015 38:259 - 65.
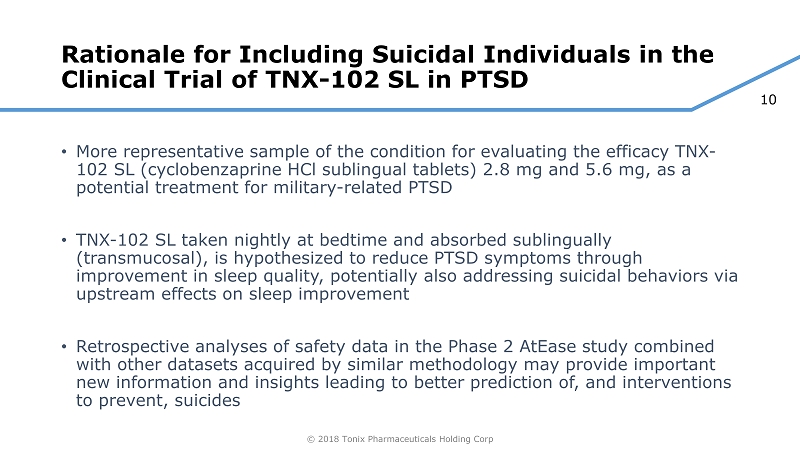
10 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Rationale for Including Suicidal Individuals in the Clinical Trial of TNX - 102 SL in PTSD • More representative sample of the condition for evaluating the efficacy TNX - 102 SL (cyclobenzaprine HCl sublingual tablets) 2.8 mg and 5.6 mg, as a potential treatment for military - related PTSD • TNX - 102 SL taken nightly at bedtime and absorbed sublingually (transmucosal), is hypothesized to reduce PTSD symptoms through improvement in sleep quality, potentially also addressing suicidal behaviors via upstream effects on sleep improvement • Retrospective analyses of safety data in the Phase 2 AtEase study combined with other datasets acquired by similar methodology may provide important new information and insights leading to better prediction of, and interventions to prevent, suicides
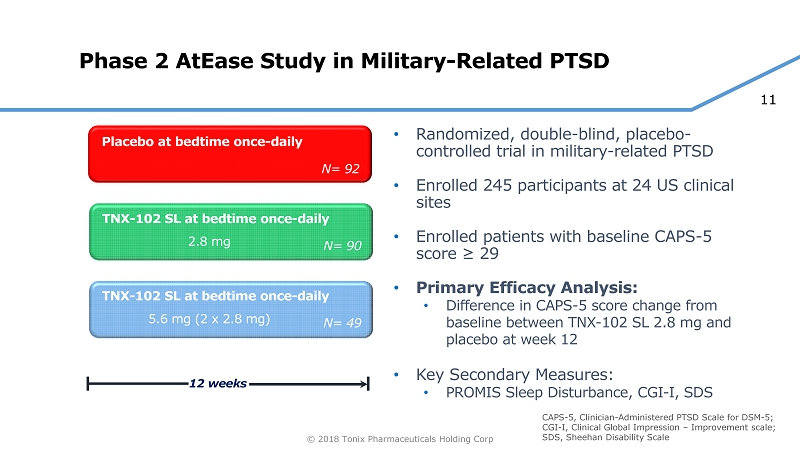
11 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Phase 2 AtEase Study in Military - Related PTSD • Randomized, double - blind, placebo - controlled trial in military - related PTSD • Enrolled 245 participants at 24 US clinical sites • Enrolled patients with baseline CAPS - 5 score ≥ 29 • Primary Efficacy Analysis: • Difference in CAPS - 5 score change from baseline between TNX - 102 SL 2.8 mg and placebo at week 12 • Key Secondary Measures: • PROMIS Sleep Disturbance, CGI - I, SDS TNX - 102 SL at bedtime once - daily Placebo at bedtime once - daily 12 weeks N= 90 TNX - 102 SL at bedtime once - daily N= 92 N= 49 2.8 mg 5.6 mg (2 x 2.8 mg) CAPS - 5, Clinician - Administered PTSD Scale for DSM - 5; CGI - I, Clinical Global Impression – Improvement scale; SDS, Sheehan Disability Scale

12 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Design of Phase 2 AtEase Study: Inclusions and Exclusions Based on SI/SB • Exclusions based on Columbia - Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C - SSRS) • Five types of Suicidal Ideation (SI) rated as present or absent during lookback period • Type 1 – Wish to be Dead • Type 2 – Non - Specific Active Suicidal Thoughts • Type 3 – Active Suicidal Ideation with Any Methods (Not Plan) without Intent to Act • Type 4 – Active Suicidal Ideation with Some Intent to Act, without Specific Plan • Type 5 – Active Suicidal Ideation with Specific Plan and Intent • Four types of Suicidal Behaviors (SB) rated as having occurred or not during lookback period • Actual Attempt • Interrupted Attempt • Aborted Attempt • Preparatory Acts or Behavior • Exclusions based on Screening MINI Module B • Suicidality score of High (≥ 17) based on past month SI and lifetime suicide attempt • YES answer to item: • B10 – Intent to act on thoughts of killing self • B11 – Intent to die as a result of a suicidal act • Meets criteria for CURRENT Suicidal Behavior Disorder (Attempt <12 months prior to Screening) – same exclusion as for C - SSRS Excluded if < 6 months prior to Screening Excluded if < 12 months prior to Screening

13 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Protocol Recommended Interventions for C - SSRS Types of Suicidal Ideation During Trial • Type 1: Standard clinical care • Types 2 and/or 3: Medical monitor recommended implementation of a Safety Planning Intervention (SPI) for any visit with these types of SI present • SPI developed by Barbara Stanley (Columbia U.) and Greg Brown (U of Penn) and adopted by US Veteran’s Administration (VA) • SPI is a brief clinical intervention aimed at mitigating suicide risk • Consists of clinician - and patient - developed list of six coping strategies and sources of support that participants can refer to and utilize to alleviate a suicidal crisis • Training in SPI provided at IM and in form of slide deck tutorial and VA SPI manual • Sites could alternatively utilize an internally - developed intervention for safety if similar in scope and purpose to the VA SPI • Types 4 and/or 5: Protocol required participant be withdrawn from the study and referred for appropriate emergency care

14 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp AtEase Study Demographics and Characteristics Sex distribution - 93% male / 7% female Index traumas 98% had trauma during military service 85% combat traumas Mean (SD) time since index trauma was 7 (3.4) yrs Deployed an average of 2.3 times Racial distribution 66% Caucasian 24% African American 2% American Indian or Alaskan Native 2% Asian Ethnic distribution 81% Not Hispanic or Latino 19% Hispanic or Latino Baseline CAPS - 5 1 and MADRS 2 scores Mean (SD) Baseline CAPS - 5 Score 39.5 (7.85) Mean (SD) Baseline MADRS Score 17.1 (5.83) Family Status 29% single 46% married or living with partner 24% separated or divorced Employment Status 62% employed 11% not able to work due to symptoms of PTSD Education 14% High school graduate or GED 57% Some college 21% College graduate 6% Graduate degree Substance Use 72% current alcohol users 38% current tobacco users 19% current THC/cannabinoid users 1 CAPS - 5, Clinician - Administered PTSD Scale for DSM - 5 2 MADRS, Montgomery - Åsberg Depression Rating Scale
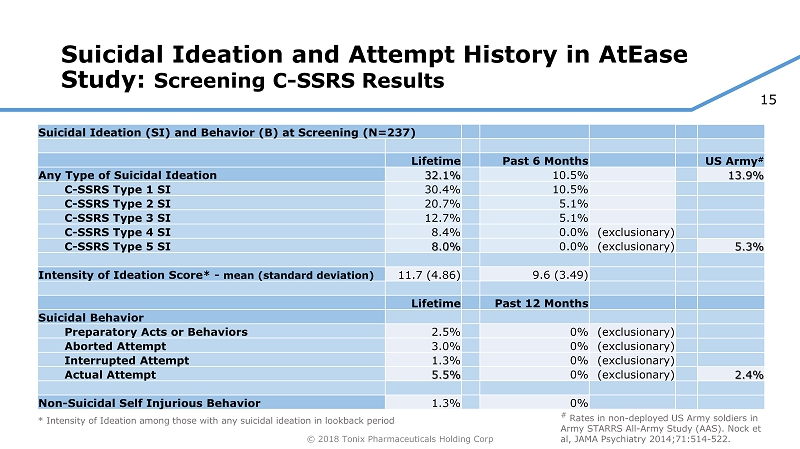
15 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Suicidal Ideation and Attempt History in AtEase Study: Screening C - SSRS Results Suicidal Ideation (SI) and Behavior (B) at Screening (N=237) Lifetime Any Type of Suicidal Ideation 32.1% C - SSRS Type 1 SI 30.4% C - SSRS Type 2 SI 20.7% C - SSRS Type 3 SI 12.7% C - SSRS Type 4 SI 8.4% C - SSRS Type 5 SI 8.0% Intensity of Ideation Score* - mean (standard deviation) 11.7 (4.86) Lifetime Suicidal Behavior Preparatory Acts or Behaviors 2.5% Aborted Attempt 3.0% Interrupted Attempt 1.3% Actual Attempt 5.5% Non - Suicidal Self Injurious Behavior 1.3% Past 6 Months 10.5% 10.5% 5.1% 5.1% 0.0% (exclusionary) 0.0% (exclusionary) 9.6 (3.49) Past 12 Months 0% (exclusionary) 0% (exclusionary) 0% (exclusionary) 0% (exclusionary) 0% US Army # 13.9% 5.3% 2.4% * Intensity of Ideation among those with any suicidal ideation in lookback period # Rates in non - deployed US Army soldiers in Army STARRS All - Army Study (AAS). Nock et al, JAMA Psychiatry 2014;71:514 - 522.
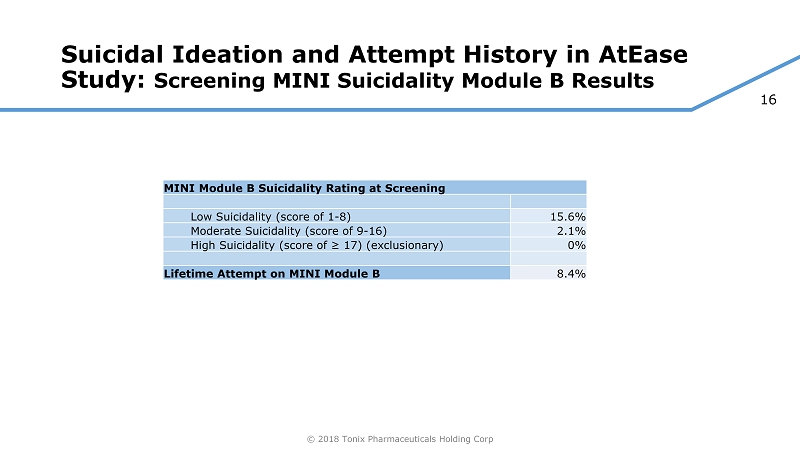
16 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Suicidal Ideation and Attempt History in AtEase Study: Screening MINI Suicidality Module B Results MINI Module B Suicidality Rating at Screening Low Suicidality (score of 1 - 8) 15.6% Moderate Suicidality (score of 9 - 16) 2.1% High Suicidality (score of ≥ 17) (exclusionary) 0% Lifetime Attempt on MINI Module B 8.4%

17 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp AtEase Study Screen Fails versus Inclusion in Individuals with SI/SB • 455 individuals were screened for the AtEase study • 210 of these were screen failed • 11 were screen failed due to SI/SB exclusions • 5 due to MINI Suicidality module score ≥ 17 • 4 due to suicidal behavior in 12 months prior to screening • 2 due to increased suicide risk based on PI judgement • 237 of 245 randomized in AtEase were in the safety population • 76 had experienced lifetime SI • 25 had experienced SI in past 6 months • 29 had lifetime suicidal behaviors • 13 of these individuals had made an actual suicide attempt • Firearm use in 12 of the 29 lifetime suicidal behaviors • 3 preparatory actions – purchasing or loading a gun with intention to kill self • 3 aborted attempts with firearm to head • 2 were interrupted when about to use firearm • 4 attempted suicide with firearm that failed to fire
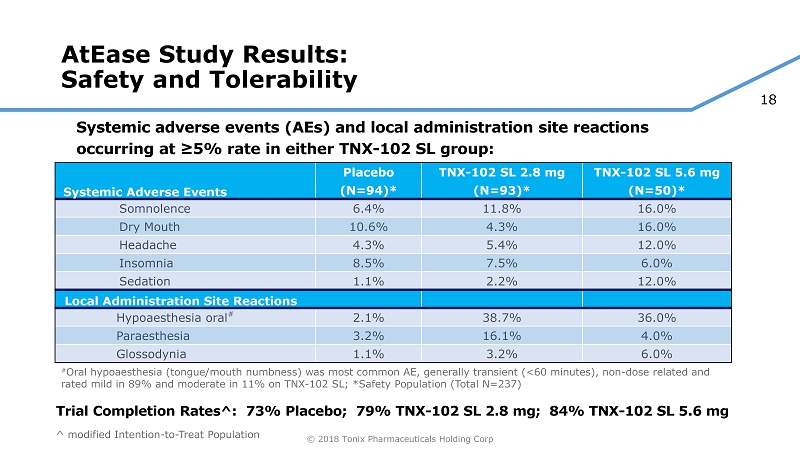
18 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp AtEase Study Results: Safety and Tolerability Systemic adverse events (AEs) and local administration site reactions occurring at ≥5% rate in either TNX - 102 SL group: Placebo TNX - 102 SL 2.8 mg TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg Systemic Adverse Events (N=94)* (N=93)* (N=50)* Somnolence 6.4% 11.8% 16.0% Dry Mouth 10.6% 4.3% 16.0% Headache 4.3% 5.4% 12.0% Insomnia 8.5% 7.5% 6.0% Sedation 1.1% 2.2% 12.0% Local Administration Site Reactions Hypoaesthesia oral # 2.1% 38.7% 36.0% Paraesthesia 3.2% 16.1% 4.0% Glossodynia 1.1% 3.2% 6.0% # Oral hypoaesthesia (tongue/mouth numbness) was most common AE, generally transient (<60 minutes), non - dose related and rated mild in 89% and moderate in 11% on TNX - 102 SL; *Safety Population (Total N=237) Trial Completion Rates^: 73% Placebo; 79% TNX - 102 SL 2.8 mg; 84% TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg ^ modified Intention - to - Treat Population

19 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Approach Taken to SI/SB Adverse Event Reporting • Any post screening increase in C - SSRS SI over Type 1 considered an adverse event • Any emergence of Type 4 and/or Type 5 SI post screening considered a serious adverse event (SAE) • Any emergence of C - SSRS - defined SB considered an SAE What was found during the AtEase study: • 4 AEs of increased SI in 3 patients » Placebo (2); TNX - 102 SL 2.8 mg (1) • 1 SAE involving C - SSRS Type 5 SI and interrupted suicide attempt » Placebo patient
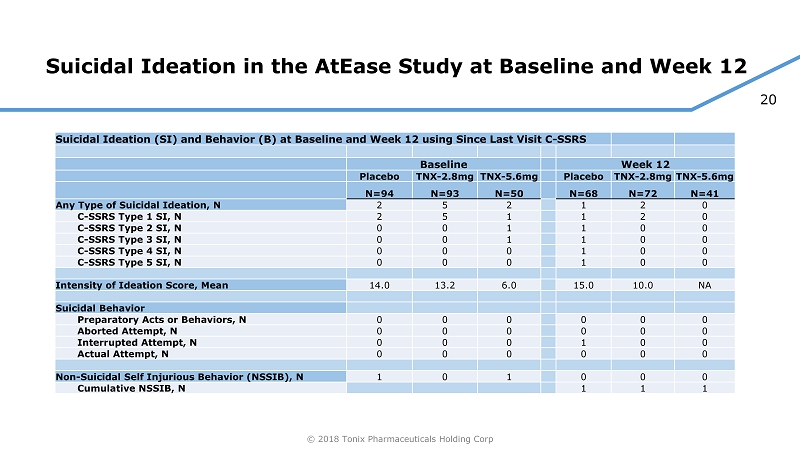
20 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Suicidal Ideation in the AtEase Study at Baseline and Week 12 Suicidal Ideation (SI) and Behavior (B) at Baseline and Week 12 using Since Last Visit C - SSRS Baseline Week 12 Placebo TNX - 2.8mg TNX - 5.6mg Placebo TNX - 2.8mg TNX - 5.6mg N=94 N=93 N=50 N=68 N=72 N=41 Any Type of Suicidal Ideation, N 2 5 2 1 2 0 C - SSRS Type 1 SI, N 2 5 1 1 2 0 C - SSRS Type 2 SI, N 0 0 1 1 0 0 C - SSRS Type 3 SI, N 0 0 1 1 0 0 C - SSRS Type 4 SI, N 0 0 0 1 0 0 C - SSRS Type 5 SI, N 0 0 0 1 0 0 Intensity of Ideation Score, Mean 14.0 13.2 6.0 15.0 10.0 NA Suicidal Behavior Preparatory Acts or Behaviors, N 0 0 0 0 0 0 Aborted Attempt, N 0 0 0 0 0 0 Interrupted Attempt, N 0 0 0 1 0 0 Actual Attempt, N 0 0 0 0 0 0 Non - Suicidal Self Injurious Behavior (NSSIB), N 1 0 1 0 0 0 Cumulative NSSIB, N 1 1 1
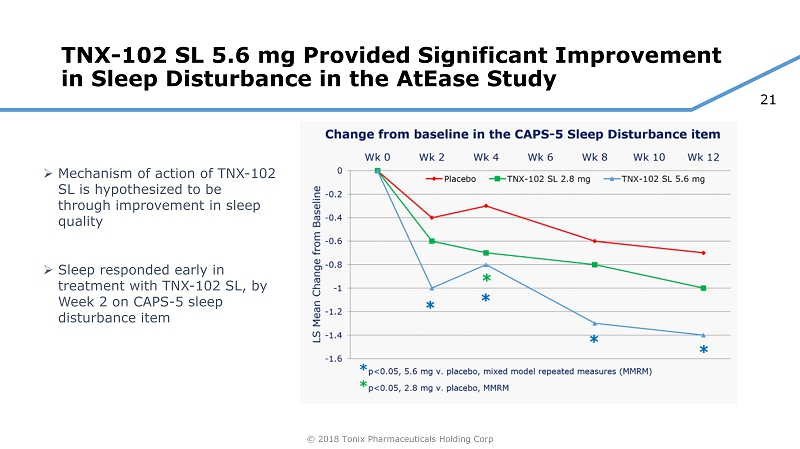
21 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg Provided Significant Improvement in Sleep Disturbance in the AtEase Study » Mechanism of action of TNX - 102 SL is hypothesized to be through improvement in sleep quality » Sleep responded early in treatment with TNX - 102 SL, by Week 2 on CAPS - 5 sleep disturbance item
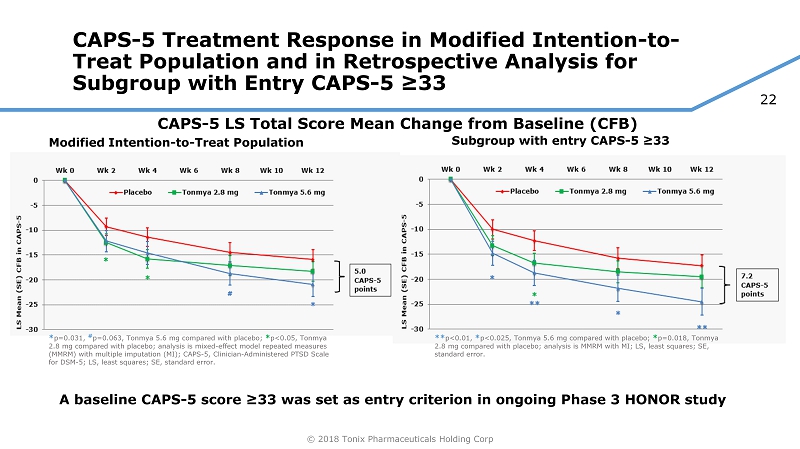
22 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp CAPS - 5 Treatment Response in Modified Intention - to - Treat Population and in Retrospective Analysis for Subgroup with Entry CAPS - 5 ≥33 A baseline CAPS - 5 score ≥33 was set as entry criterion in ongoing Phase 3 HONOR study Modified Intention - to - Treat Population Subgroup with entry CAPS - 5 ≥33 CAPS - 5 LS Total Score Mean Change from Baseline (CFB) * p=0.031, # p=0.063, Tonmya 5.6 mg compared with placebo; * p<0.05, Tonmya 2.8 mg compared with placebo; analysis is mixed - effect model repeated measures ( MMRM) with multiple imputation (MI) ; CAPS - 5, Clinician - Administered PTSD Scale for DSM - 5; LS, least squares; SE, standard error. ** p<0.01, * p<0.025, Tonmya 5.6 mg compared with placebo; * p=0.018, Tonmya 2.8 mg compared with placebo; analysis is MMRM with MI ; LS, least squares; SE, standard error.

23 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp CAPS - 5 Item 16 (E2) – New to DSM - 5/CAPS - 5 • Reckless or self - destructive behavior • Risk • “In the past month/week, have there been times when you were taking more risks or doing things that might have caused you harm? • Can you give me some examples? • How much risk do you take? (How dangerous are these behaviors? Were you injured or harmed in some way?)” • Frequency • How often have you taken these kinds of risks in the past month /week? (# of times) • Trauma - relatedness • Did this behavior start or get worse after (index trauma)? • As per DSM - 5, intended for behaviors such as dangerous driving, excessive alcohol or drug use, and self - injurious or suicidal behavior • Due to exclusion of SB in past year and very low rates of any non - suicidal self injurious behavior or SB during trial, item appeared to be primarily indexing dangerous, high risk activities in prior week that had developed or got worse after index trauma(s)
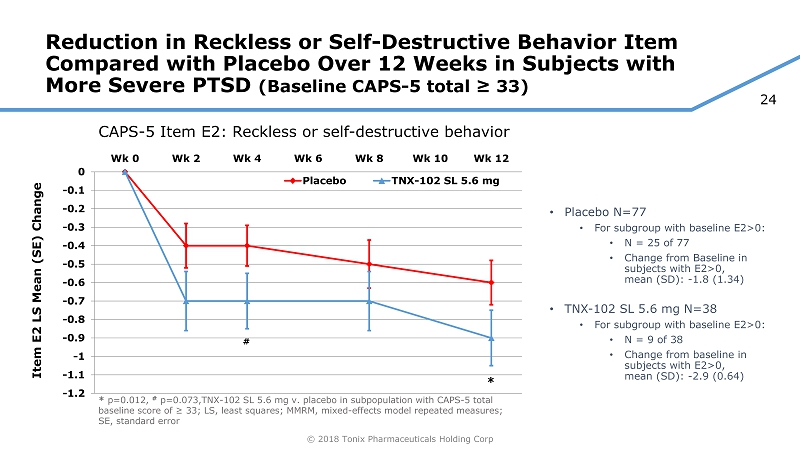
24 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Reduction in Reckless or Self - Destructive Behavior Item Compared with Placebo Over 12 Weeks in Subjects with More Severe PTSD (Baseline CAPS - 5 total ≥ 33) • Placebo N=77 • For subgroup with baseline E2>0: • N = 25 of 77 • Change from Baseline in subjects with E2>0, mean (SD): - 1.8 (1.34) • TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg N=38 • For subgroup with baseline E2>0: • N = 9 of 38 • Change from baseline in subjects with E2>0, mean (SD): - 2.9 (0.64) -1.2 -1.1 -1 -0.9 -0.8 -0.7 -0.6 -0.5 -0.4 -0.3 -0.2 -0.1 0 Wk 0 Wk 2 Wk 4 Wk 6 Wk 8 Wk 10 Wk 12 Item E2 LS Mean (SE) Change Placebo TNX-102 SL 5.6 mg # * p=0.012, # p=0.073, TNX - 102 SL 5.6 mg v. placebo in subpopulation with CAPS - 5 total baseline score of ≥ 33; LS, least squares; MMRM, mixed - effects model repeated measures; SE, standard error * CAPS - 5 Item E2: Reckless or self - destructive behavior

25 © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp Conclusions about Including Suicidal Individuals in Phase 2 Trial of Military - Related PTSD • AtEase military - related PTSD sample had higher lifetime rates of SI/B compared with non - deployed Army sample • Rates of since - last - visit SI and SB during study were extremely low, such that meaningful statistical inferences are not possible • Employing Safety Planning Intervention (SPI) for C - SSRS Types 2 and/or 3 helpful for ensuring intensive clinical management for safety • High risk behaviors were reduced with treatment in more severe subpopulation • Non - exclusion of PTSD participants with history of SI/B greatly strengthens generalizability of any treatment findings for this population • Future outpatient studies could reduce SI/SB exclusions further, such as no C - SSRS Types 4 or 5 in past month and no SB in past 3 months • Inclusion of individuals with SI/B in pharmacotherapy trials such as AtEase provides critical data for meta - analyses aimed at better understanding of the predictors of suicide, reducing the risk, and facilitating the development of drug candidates for the prevention of death by suicide

26 Thank you…! © 2018 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp To our research participants for their collaboration in the AtEase study! To our site PIs and Staff! To Tonix personnel responsible for AtEase : » Seth Lederman, Judy Gendreau, Ashild Peters, Perry Peters, Gregory Sullivan And to key consultants: » Pauliana Hall, R. Michael Gendreau, Amy Schaberg , Frank Weathers, Jonathan Davidson