
Exhibit 99.02

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Using Synthetic Biology to Battle Mpox Symposium to Honor Prof. David Evans on His Retirement Seth Leder man, M.D. Version P0594 Sept 6, 2024 (Doc 1505)

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Cautionary Note on Forward - Looking Statements Certain statements in this presentation regarding strategic plans, expectations and objectives for future operations or results are “forward - looking statements” as defined by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be identified by the use of forward - looking words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “forecast,” “estimate” and “intend,” among others. These forward - looking statements are based on Tonix’s current expectations and actual results could differ materially. There are a number of factors that could cause actual events to differ materially from those indicated by such forward - looking statements. These factors include, but are not limited to, the risks related to failure to obtain FDA clearances or approvals and noncompliance with FDA regulations; delays and uncertainties caused by the global COVID - 19 pandemic; risks related to the timing and progress of clinical development of our product candidates; our need for additional financing; uncertainties of patent protection and litigation; uncertainties of government or third party payor reimbursement; limited research and development efforts and dependence upon third parties; and substantial competition. As with any pharmaceutical under development, there are significant risks in the development, regulatory approval and commercialization of new products. The forward - looking statements in this presentation are made as of the date of this presentation, even if subsequently made available by Tonix on its website or otherwise. Tonix does not undertake an obligation to update or revise any forward - looking statement, except as required by law. Investors should read the risk factors set forth in the Annual Report on Form 10 - K for the year ended December 31, 202 3 , as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on April 1 , 202 4 , and periodic reports and current reports filed with the SEC on or after the date thereof. All of Tonix's forward - looking statements are expressly qualified by all such risk factors and other cautionary statements.

3 © 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. In 1798, Dr. Edward Jenner Described the “Virus” that Causes Cow Pox and Identified its Utility in Preventing Smallpox 3 • Jenner, E. (1798) “An Inquiry Into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae , a Disease Discovered in Some of the Western Counties of England, Particularly Gloucestershire, and Known by the Name of the Cow Pox” • Known as “The Inquiry”… • Jenner observed milkmaids were protected from smallpox • Cow Pox was a mild illness in humans that provided protection (later known as immunity ) “Cow Pox” was the name of a disease in cows that could transfer to humans and cause sores

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. • Jenner "vaccinated” healthy individuals with material from the lesions, which he called “vaccine” (from vacca , Latin for “cow”) • The p ustule matter from “cow pox” sores on a milkmaid’s hands; conferred protection against future challenges with smallpox virus inoculation • Jenner suspected that the agent (“infectious principle”) causing cow pox, which he called vaccinia originated in horses and had been transferred from horses to cows’ udders by the hands of farriers Edward Jenner Successfully Used Vaccination to Protect Against Smallpox 4 The College of Physicians of Philadelphia. Accessed July 15, 2021. https:/ /w w w.historyofvaccines.org

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. First Live Virus Vaccine: Edward Jenner’s Inquiry 1 (1798) – 1/2 “There is a disease to which the Horse from his state of domestication is frequently subject. The Farriers have termed it the Grease . It is an inflammation and swelling in the heel, from which issues matter 2 possessing properties of a very peculiar kind, which seems capable of generating a disease in the Human Body (after it has undergone the modification 3 I shall presently speak of), which bears so strong a resemblance to the Small Pox, that I think it highly probable it may be the source of that disease.” 1 Jenner, E. “An Inquiry Into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae , a Disease Discovered in Some of the Western Counties of England, Particularly Gloucestershire, and Known by the Name of the Cow Pox (p 2 - 3.) 2 Vaccine virus 3 Passage in cows 5

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. First Live Virus Vaccine: Edward Jenner’s Inquiry 1 (1798) – 2/2 1 Jenner, E. “An Inquiry Into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae , a Disease Discovered in Some of the Western Counties of England, Particularly Gloucestershire, and Known by the Name of the Cow Pox (p 3.) “In this Dairy Country a great number of Cows are kept, and the office of milking is performed indiscriminately by Men and Maid Servants. One of the former having been appointed to apply dressings to the heels of a Horse affected with the Grease , and not paying due attention to cleanliness, incautiously bears his part in milking the Cows, with some particles of the infectious matter adhering to his fingers. When this is the case, it commonly happens that a disease is communicated to the Cows, and from the Cows to the Dairy - maids, which spreads through the farm until most of the cattle and domestics feel its unpleasant consequences. The disease has obtained the name of the Cow Pox .” 6

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Loy’s “ Account of some experiments 1 (1801) “This fact induces me to suspect, that two kinds of Grease exist, differing from each other in the power of giving disease to the human or brute animal: and there is another circumstance which renders this supposition probable. The horses that communicated the infection to their dressers, were affected with a general, as well as a topical, disease. The animals, at the commencement of their disease, were evidently in a feverish state, from which they were relived as soon as the complaint appeared at their heels, and an eruption upon their skin. The horse , too, from whom the infectious matter was procured for inoculation, had a considerable indisposition, previous to the disease at his heels, which was attended, as in the others, with an eruption over the greatest part of his body: but those that did not communicate the diseases at all, had a local affection only.” 1 Loy JG. An account of some experiments on the origin of the cow - pox: Whitby; 1801. (p 20 - 21.) 7

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Equination 1 : Use of Smallpox Vaccines Directly from Horse Lesions (Without Passage Through Cows) Both Jenner and Loy used vaccine from horses; subsequently “ Equination ” was used in Europe in parallel with “vaccination” − Jenner believed that his “cowpox” or “vaccinia” came from horses with “Grease” Horsepox isolated from a sick horse in Mongolia in 1976 − Like many other poxviruses, natural host is likely rodents (mice or voles) − No cases reported in >30 years, some believe it to be extinct; eliminated through improved animal husbandry 1 Esparza J, Schrick L, Damaso CR, Nitsche A. Equination (inoculation of horsepox): An early alternative to vaccination (inoculation of cowpox) and the potential role of horsepox vir us in the origin of the smallpox vaccine. Vaccine . 2017 Dec 19;35(52):7222 - 7230. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Review. PMID:29137821 8
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 2006 Sequence and Analysis of the Horsepox Genome 1 9 “ It is likely that a once naturally circulating but now rare VACV - like virus(s) from which current strains are derived was introduced as a vaccine virus, and the agent of horsepox has been surmised as a likely candidate ( Baxby , D 1981 2 ). Indeed, apparently Edward Jenner believed that his vaccine originated from the “grease” infection found in the heels of horses , and the use of horse - derived material for use as vaccines is documented ( Baxby , ibid. , Fenner F, 1989 3 ). ” 1 Tulman ER, et al. 2006. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol 80:9244 – 9258 . 2 Baxby , D. 1981. Jenner’s smallpox vaccine: the riddle of vaccinia virus and its origin. Heinemann Educational Books Ltd., London, Uni ted Kingdom. 3 Fenner , F., R. Wittek , and K. Dumbell . 1989. The orthopoxviruses . Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, Calif.

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. 2015 Genetic Analysis of Vaccinia Vaccines: Horsepox - like Virus Ancestor? 1 10 “The biological origin of VACV is uncertain, although it has been suggested that a horsepox - like virus was an ancestor, even though a surviving horsepox virus (HPXV) genome harbors many extra genes ( Tulman ER, 2006 2 ). This hypothesis is supported by Jenner’s report that he obtained his later inocula from an infection in horses called “grease” ( Baxby D, 1977 3 )” 1 Qin, L., Favis , N., Famulski , J. & Evans, D. H. Evolution of and evolutionary relationships between extant vaccinia virus strains. J. Virol . 89 , 1809 – 1824 (2015) 2 Tulman ER, et al. 2006. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol 80:9244 – 9258 . 3 Baxby D. 1977. The origins of vaccinia virus. J Infect Dis 136:453 – 455. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/136.3.453.
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. David Evans 1 : Speciation and Gene Loss in Vaccinia Evans in (Qin et al): , “…the process of speciation appears to be associated with gene loss. ” − Larger virus − “ Relationship between DPP25 and horsepox virus. An important aspect of poxvirus evolutionary modeling concerns the hypothesis that as viruses spread into new biological niches, the process of speciation appears to be associated with gene loss (3). If this is true, then the simplest evolutionary scheme would involve a DPP25 - like virus evolving from an even larger virus. Horsepox virus (HPXV) is the largest known example of what is still clearly a vaccinia virus, if one defines this assignment based upon a relationship supported by phylogenetic trees, and perhaps retains some resemblance to a hypothetical common ancestor. By using a dot matrix plot, it can be seen that HPXV and DPP25 share the same gene content and gene order from DVX_014 (vaccinia virus growth factor) to DVX_213 as well as from ORFs DVX_214 to DVX_216 (containing fragments of a Kelch - like protein) (Table 3). However, DPP25 also encodes duplicated segments of DNA bearing the genes DVX_010 to DVX_013 inboth the right and left TIRs, whereas this sequence is found only in the right end of HPXV (Fig. 3A, deletion 3). Compared to HPXV, DPP25 also bears a 10.7 - kbp deletion near the left TIR boundary and a 5.5 - kbp deletion near the right TIR boundary (Fig. 3A, deletions 1 and 2, respectively). (The 5.5 - and 10.7 - kbp deletions differentiate HPXV from all other vaccinia virus strains and are discussed in greater detail below.) Collectively, these data suggest that DPP25/CL3 shares a unique sequence with HPXV, located near the right TIR boundary, but that the overall genome structures have been impacted by events that have changed the location of the TIR boundaries, inverted and duplicated sequences now located in the TIRs, and deleted two large segments of DNA.” 11 1 Qin, L., Favis , N., Famulski , J. & Evans, D. H. Evolution of and evolutionary relationships between extant vaccinia virus strains. J. Virol . 89 , 1809 – 1824 (2015 )
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Synthesis of Horsepox (HPXV, TNX - 801) 2018 1 12 1 Noyce RS, Lederman S, Evans DH. PLoS One . 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0188453. doi : 10.1371/journal.pone.0188453. PMID: 29351298; PMCID: PMC5774680.
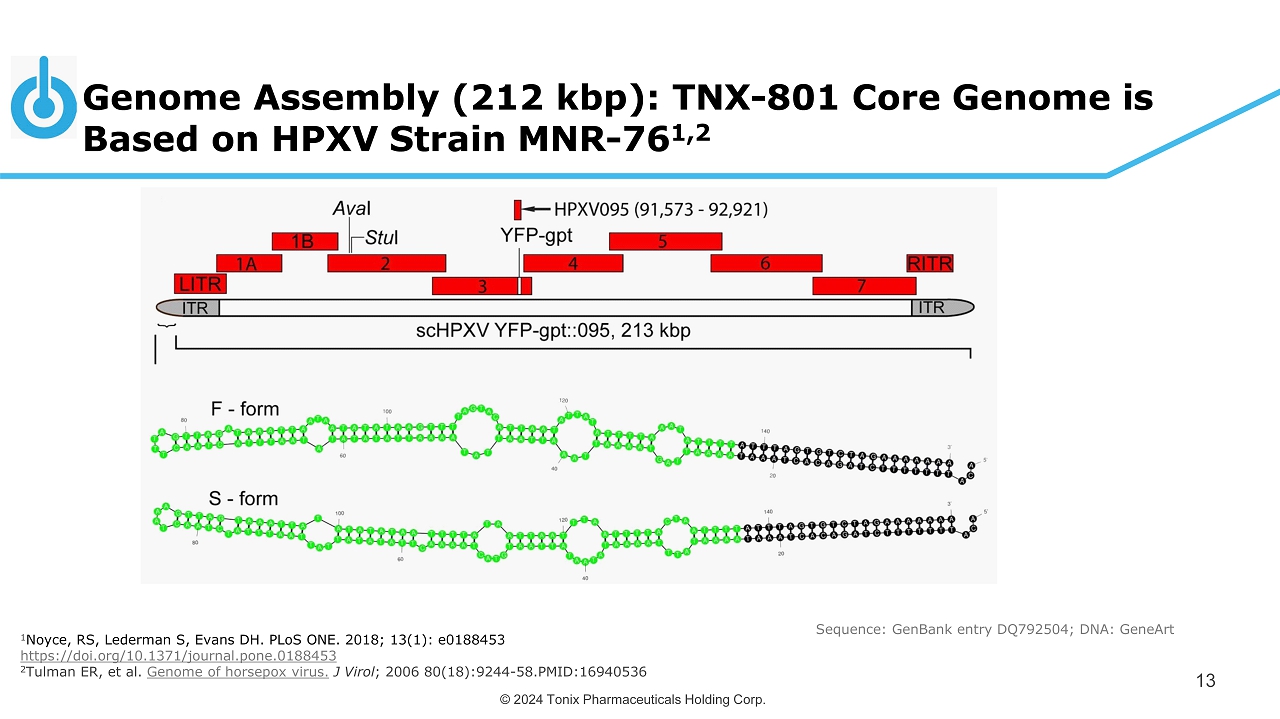
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Genome Assembly (212 kbp ): TNX - 801 Core Genome i s Based on HPXV Strain MNR - 76 1,2 13 Sequence: GenBank entry DQ792504; DNA: GeneArt 1 Noyce, RS, Lederman S, Evans DH. PLoS ONE. 2018; 13(1): e0188453 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188453 2 Tulman ER, et al. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol ; 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 (Live HPXV for Percutaneous Administration) 14 Vaccine based on sequence of isolated horsepox (HPXV) clone 1 − Synthesized 2 since 1976 isolate was not available outside of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) − No new gene elements − Coding sequence identical to HPXV Small plaque size in culture − Appears identical to U.S. CDC publication of 1976 horsepox isolate 3 Question: will “horsepox” perform as a vaccine similar to “Jenner’s vaccinia” and 20 th century vaccinia vaccines? − Need to evaluate tolerability and activity in animal models 1 Tulman ER, et al. J Virol . 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 2 Noyce RS, et al.. PLoS One . 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0188453 3 Trindade GS , et al. Viruses 2016 Dec 10;8(12). pii : E328. PMID:27973399 PMCID: 10.3390/v8120328
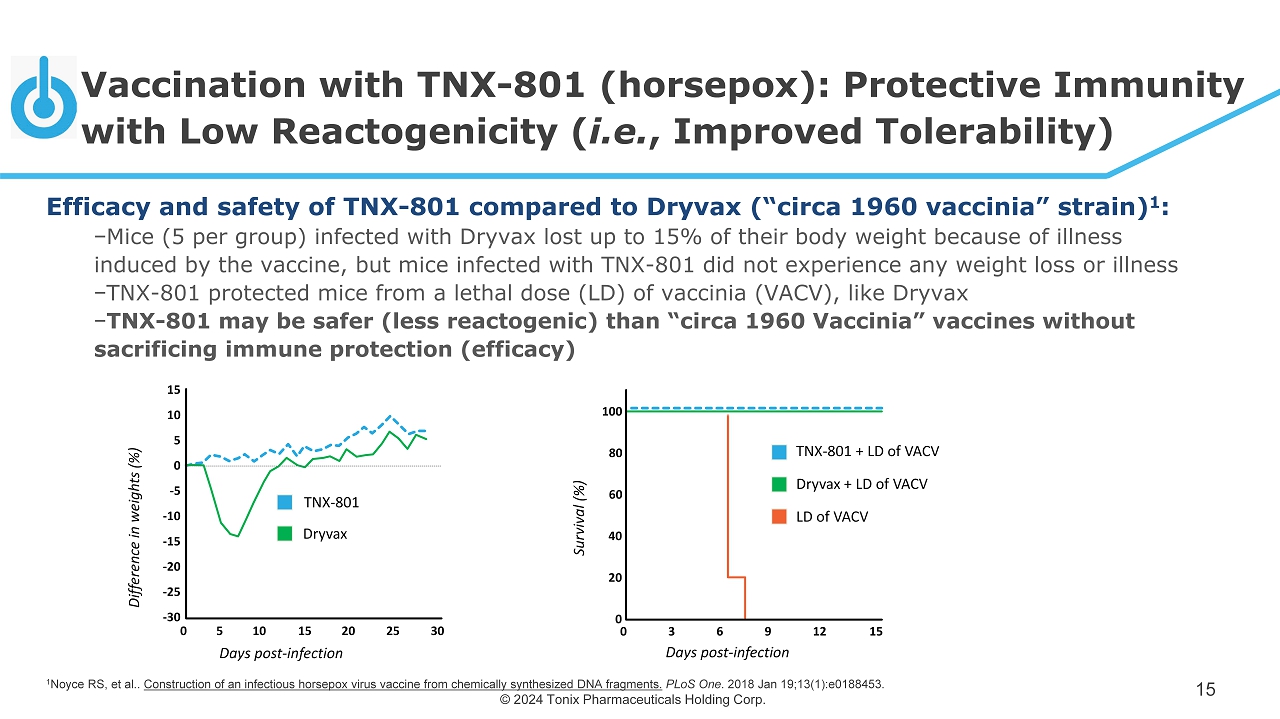
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Vaccination with TNX - 801 ( horsepox ): Protective Immunity with Low Reactogenicity ( i.e. , Improved Tolerability) 15 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 Days post - infection Survival (%) TNX - 801 + LD of VACV Dryvax + LD of VACV LD of VACV 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 15 10 5 0 - 5 - 10 - 15 - 20 - 25 - 30 Days post - infection Difference in weights (%) TNX - 801 Dryvax 1 Noyce RS, et al.. Construction of an infectious horsepox virus vaccine from chemically synthesized DNA fragments. PLoS One . 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0188453. Efficacy and safety of TNX - 801 compared to Dryvax (“circa 1960 vaccinia” strain) 1 : − Mice (5 per group) infected with Dryvax lost up to 15% of their body weight because of illness induced by the vaccine, but mice infected with TNX - 801 did not experience any weight loss or illness − TNX - 801 protected mice from a lethal dose (LD) of vaccinia (VACV), like Dryvax − TNX - 801 may be safer (less reactogenic) than “circa 1960 Vaccinia” vaccines without sacrificing immune protection (efficacy)
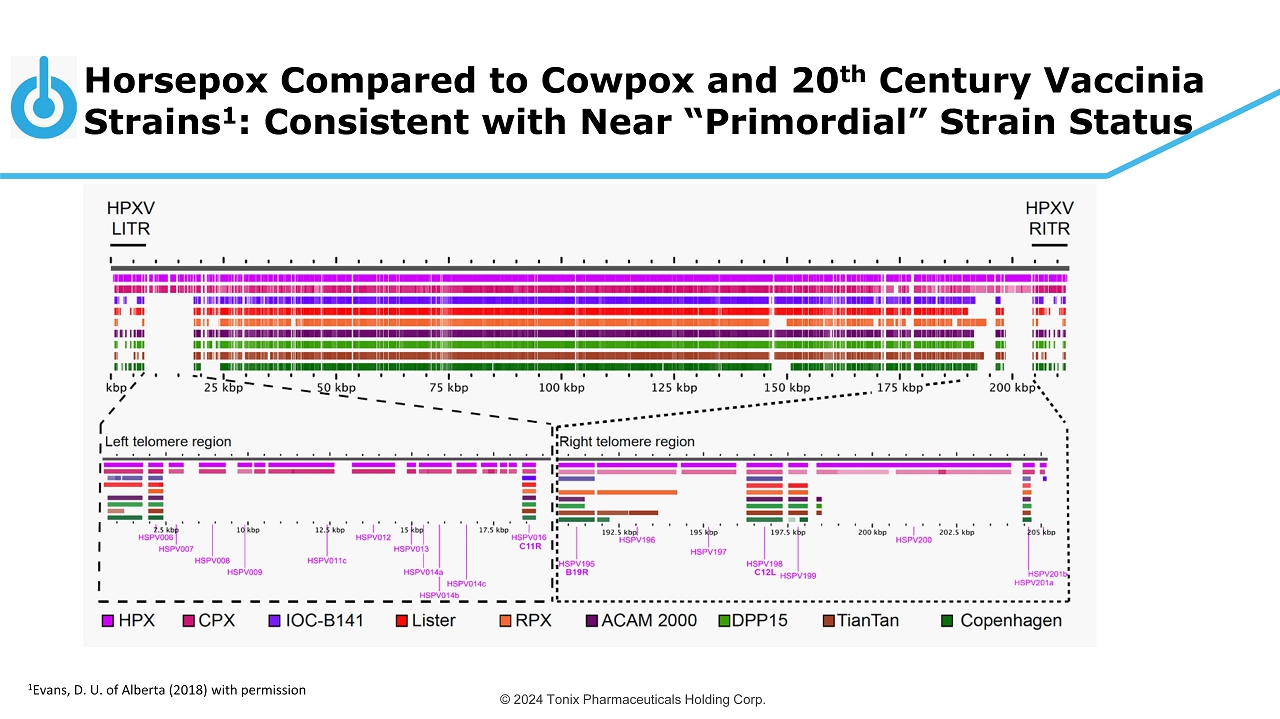
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Horsepox Compared to Cowpox and 20 th Century Vaccinia Strains 1 : Consistent with Near “Primordial” Strain Status 1 Evans, D. U. of Alberta (2018) with permission
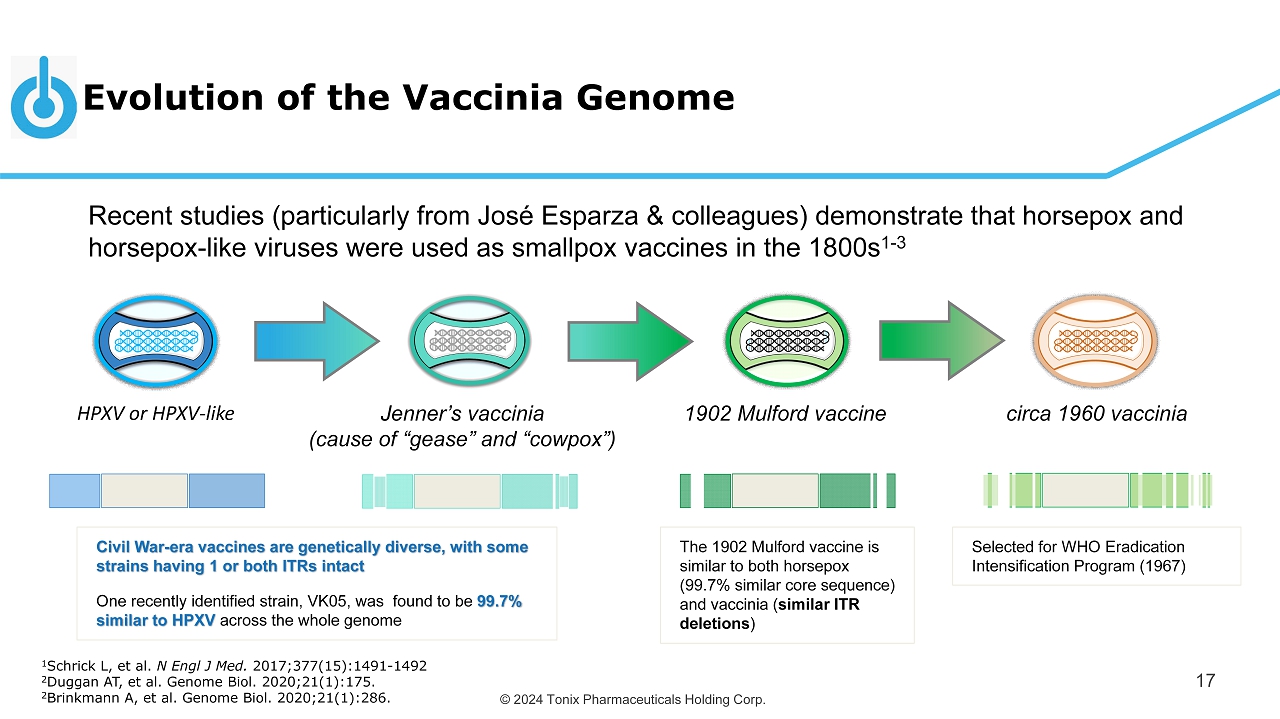
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Evolution of the Vaccinia Genome 17 Recent studies (particularly from José Esparza & colleagues ) demonstrate that horsepox and horsepox - like viruses were used as smallpox vaccines in the 1800s 1 - 3 HPXV or HPXV - like Jenner’s vaccinia (cause of “ gease ” and “cowpox”) 1902 Mulford vaccine circa 1960 vaccinia The 1902 Mulford vaccine is similar to both horsepox (99.7% similar core sequence) and vaccinia ( similar ITR deletions ) Selected for WHO Eradication Intensification Program (1967) Civil War - era vaccines are genetically diverse, with some strains having 1 or both ITRs intact One recently identified strain, VK05, was found to be 99.7% similar to HPXV across the whole genome 1 Schrick L, et al. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(15):1491 - 1492 2 Duggan AT, et al. Genome Biol. 2020;21(1):175. 2 Brinkmann A, et al. Genome Biol. 2020;21(1):286.

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Horsepox: Relationship to Jenner’s Vaccinia Horsepox environmental isolate sequenced in 2006 shares a common ancestor with vaccinia and could be considered a strain of vaccinia − Similar to cowpox with “intact” inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) – could be considered a primordial strain of vaccinia − TNX - 801 has strong homology in core with Mulford 1902 vaccinee 1 − TNX - 801 has 99.7% colinear identity with “ circa 1860 vaccinia ” smallpox vaccine VK05, including the LTRs/ITRs that contain host control elements 2,3 Genetic analysis of early vaccines indicates that “horsepox” is closely related to Edward Jenner’s vaccinia from 1796 − Strong evidence linking a horsepox - like virus as progenitor to circa 1960 vaccinia − circa 1960 “vaccinia” evolved during the 220 years it was propagated by primitive methods – Propagated for over 120 years before “viruses” were characterized − Selected for reactogenicity and growth (replication) 1 Schrick, L. et al An Early American Smallpox Vaccine Based on Horsepox N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1491 2 Tulman ER, et al. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol ; 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 3 Brinkmann A et al, Genome Biol ogy 2020 ; 21:286 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059 - 020 - 02202 - 0 18
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Deduced Relationship of Horsepox with “Jenner’s Vaccinia” and “20 th Century Vaccinia” Vaccines 1976 Mongolian Field Isolate Arm - to - arm Molecular Biology “Vaccine Farms” Cow production started ~1875: Selection for Growth, Reactivity or Increased Virulence Deletions TNX - 801 Less virulent than 20 th Century Vaccinia “20 th Century Vaccinia” More virulent than horsepox Horsepox Progenitor 1860 US Civil War Vaccine VK05 “Jenner’s Vaccinia”
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 (Live - virus Horsepox Vaccine for Percutaneous Administration) 20 Vaccine based on sequence of isolated horsepox (HPXV) clone 1 − Synthesized 2 since 1976 isolate was not available outside of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) − No new gene elements − Coding sequence identical to HPXV Small plaque size in culture − Appears identical to U.S. CDC publication of 1976 horsepox isolate 3 Question: will “horsepox” perform as a vaccine similar to “Jenner’s vaccinia”? − Need to evaluate tolerability and activity in animal models 1 Tulman ER, et al. J Virol . 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 2 Noyce RS, et al.. PLoS One . 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0188453 3 Trindade GS , et al. Viruses 2016 Dec 10;8(12). pii : E328. PMID:27973399 PMCID: 10.3390/v8120328

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 Immunogenicity and Efficacy in Macaques - 2023 21 Noyce RS, et al. Viruses . 2023 Jan 26;15(2):356. doi : 10.3390/v15020356. PMID: 36851570; PMCID: PMC9965234.
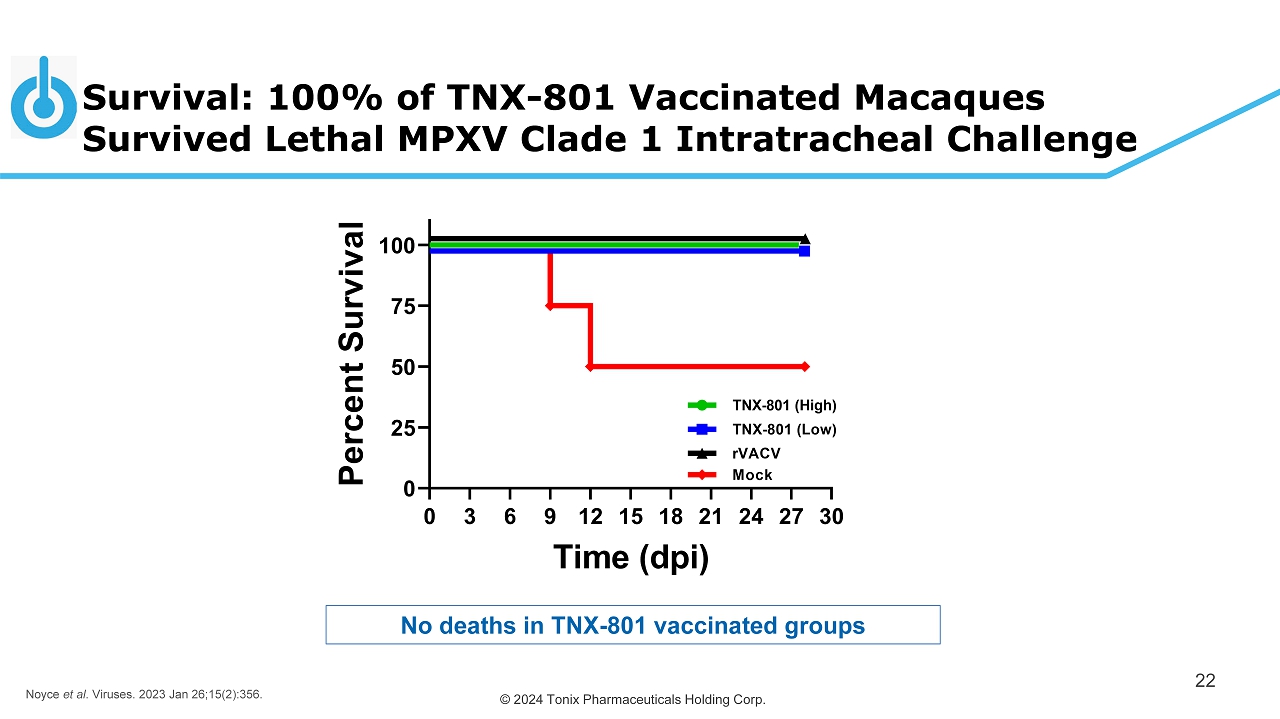
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Survival: 100% of TNX - 801 Vaccinated Macaques Survived Lethal MPXV Clade 1 Intratracheal Challenge 22 No deaths in TNX - 801 vaccinated groups Noyce et al . Viruses. 2023 Jan 26;15(2):356.
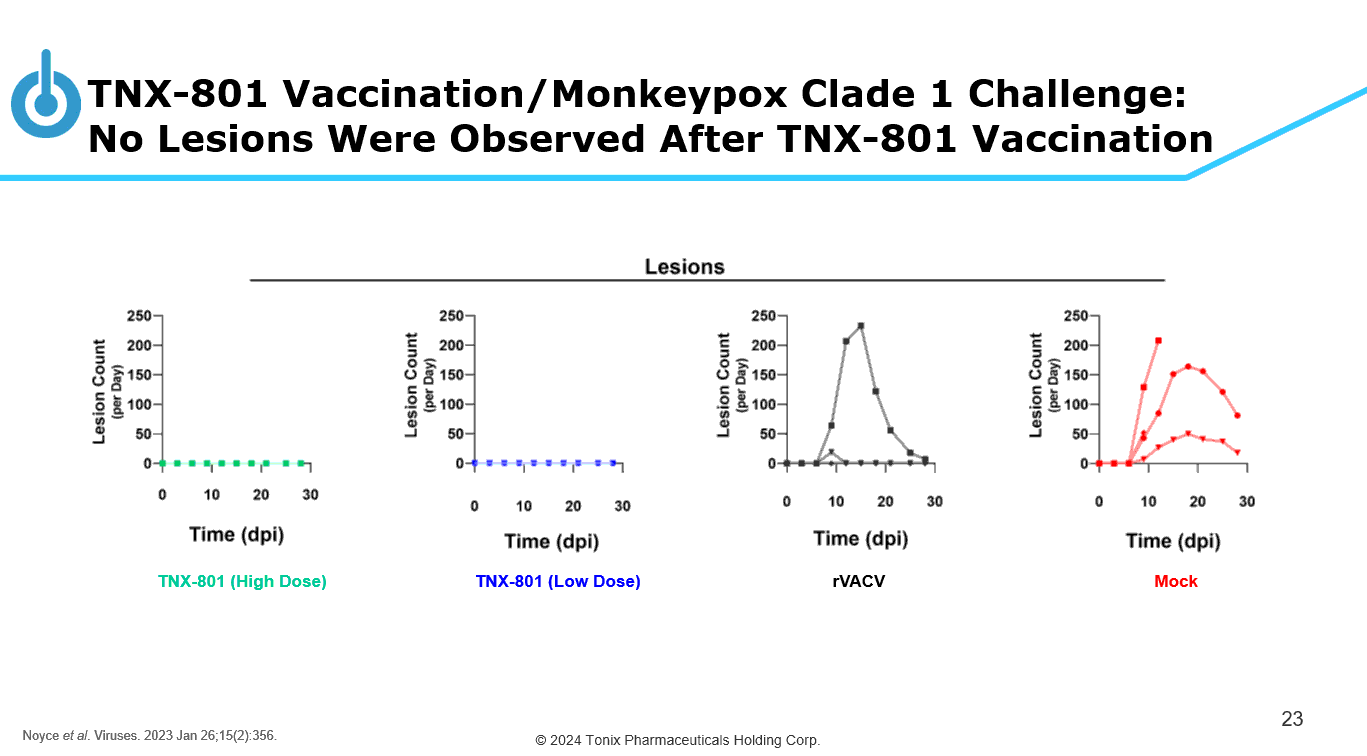
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 Vaccination/Monkeypox Clade 1 Challenge: No Lesions Were Observed After TNX - 801 Vaccination 23 TNX - 801 (High Dose) TNX - 801 (Low Dose) rVACV Mock Noyce et al . Viruses. 2023 Jan 26;15(2):356.
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 Vaccination: Minimal Monkeypox Virus Shedding 24 TNX - 801 (High Dose) TNX - 801 (Low Dose) rVACV Mock Potential to Reduce Forward Transmission Noyce et al . Viruses. 2023 Jan 26;15(2):356.

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Conclusions from Macaque Monkeypox Challenge Study 25 • A single dose of TNX - 801 (horsepox) vaccination was well tolerated ‒ No severe adverse events ‒ Tolerability compares favorably to ACAM2000 – recently approved by US FDA for mpox 1 • TNX - 801 vaccination via traditional route (scarification) was immunogenic (“take”) • All NHPs (TNX - 801 and rVACV vaccinated) survived lethal challenge • No clinical disease was observed (lesions) • Provided strong protection against virus shedding, viremia, and weight loss ‒ Activity compares favorably to MVA (non - replicating) 2 vaccinia or recent mRNA vaccine 3 • 1 August 30, 2024. Reuters. “US FDA approves Emergent's smallpox vaccine for people at high risk of mpox”. https://www.msn.com/en - us/health/other/us - fda - approves - emergent - s - smallpox - vaccine - for - people - at - high - risk - of - mpox/ 2 Zaeck LM, et al. Low levels of monkeypox virus - neutralizing antibodies after MVA - BN vaccination in healthy individuals. Nat Med. 2023 Jan;29(1):270 - 278. doi : 10.1038/s41591 - 022 - 02090 - w. Epub 2022 Oct 18. PMID: 36257333; PMCID: PMC9873555. 3 Mucker et al., (in press) Comparison of protection against mpox following mRNA or modified vaccinia Ankara vaccination in non hum an primates, Cell (2024), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.043

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 in Primary Cell Lines and Immunocompromised Mice – 2023 ( BioRxiv ) 26 Trefry , SV et al. bioRxiv 2023.10.25.564033; doi : https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.10.25.564033

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 has Reduced Virulence Relative to “20 th Century Vaccinia Vaccines” 27 Comparisons in vitro: 1) Plaque phenotype: VACV ( 3 - 4 mm) vs. TNX - 801 ( 1 - 2 mm) 2) Multi - step growth kinetics: ▪ Immortalized cell lines: TNX - 801 10 - to 1 00 - fold less virulent ▪ Human primary cell lines: TNX - 801 10 - to 100 - fold less virulent Comparisons in vivo : 1) Assessed TNX - 801 attenuation in immunocompromised murine models (C57BL/6 ifnar - / - and C57BL/6 ifnar - / - / ifngr - / - ) : ▪ TNX - 801 is >100 - to 1,000 - fold less virulent than VACV strains ▪ TNX - 801 is indistinguishable from mock treated animals in immunocompromised model
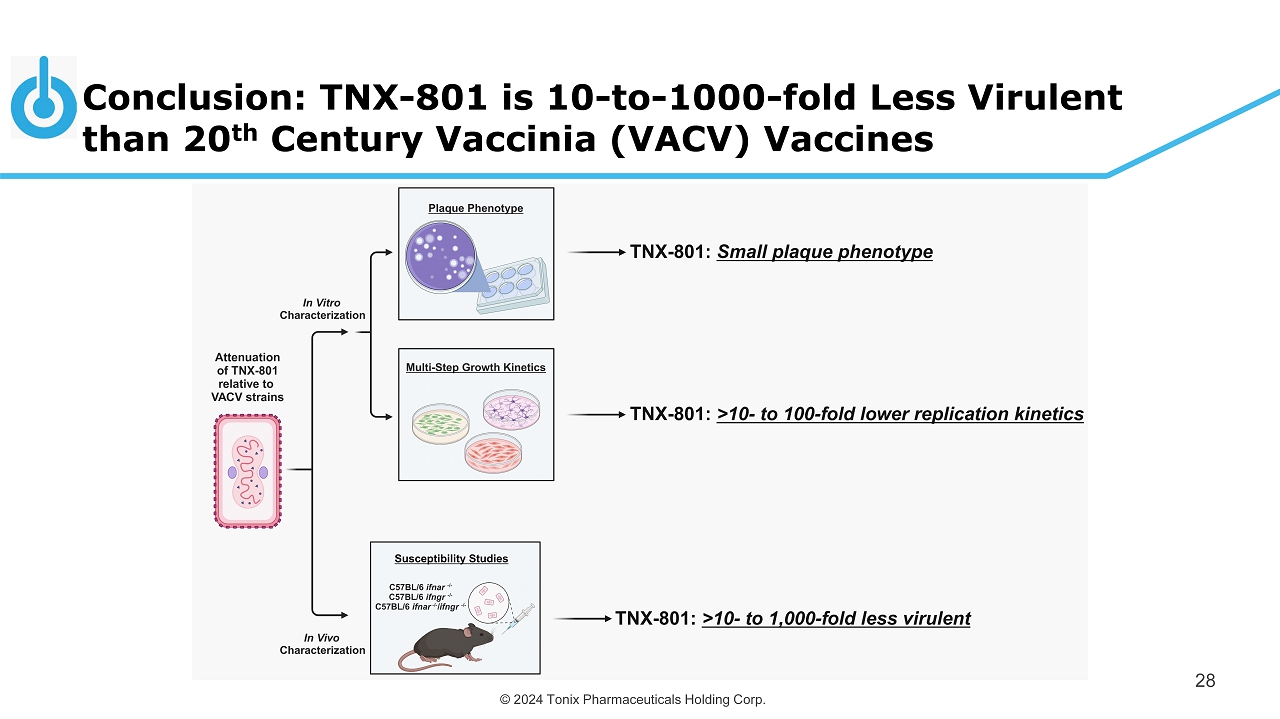
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Conclusion: TNX - 801 is 10 - to - 1000 - fold Less Virulent than 20 th Century Vaccinia (VACV) Vaccines 28
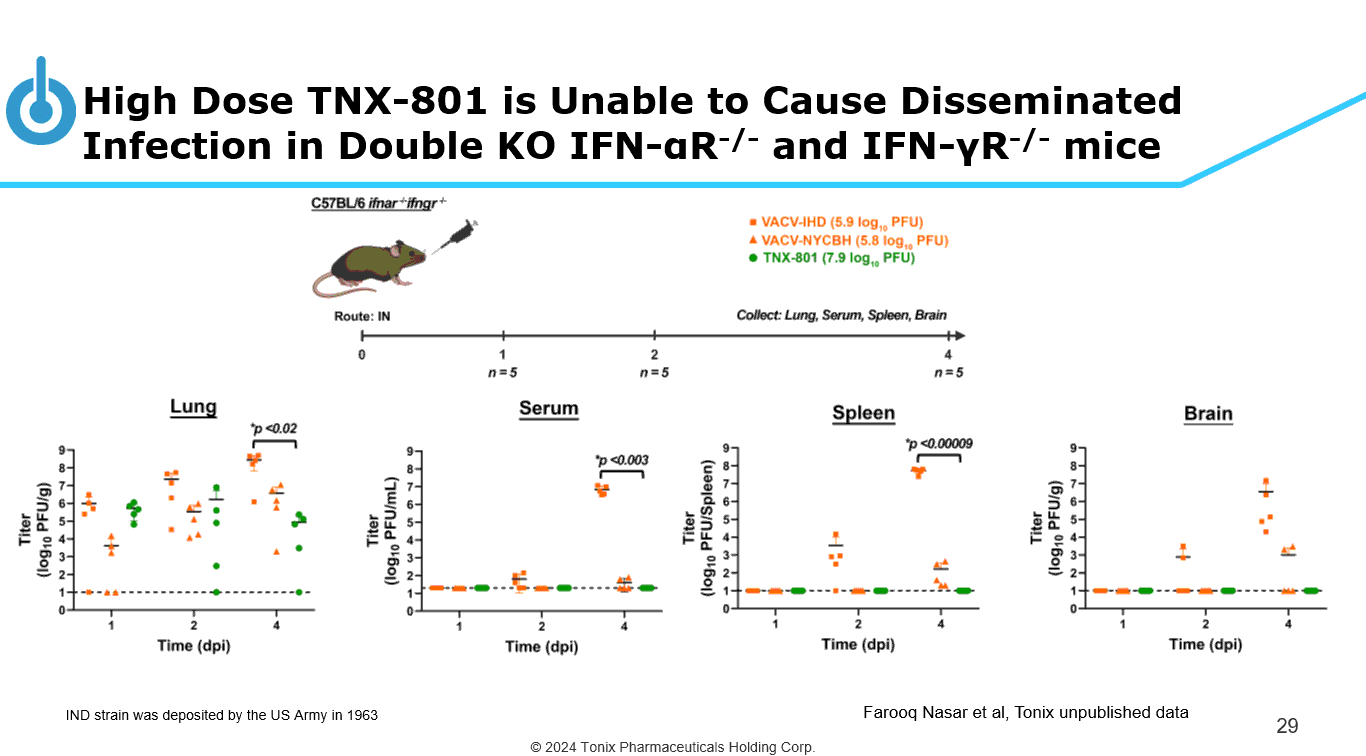
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. High Dose TNX - 801 is Unable to Cause Disseminated Infection in Double KO IFN - α R - / - and IFN - γ R - / - mice 29 IND strain was deposited by the US Army in 1963 Farooq Nasar et al, Tonix unpublished data
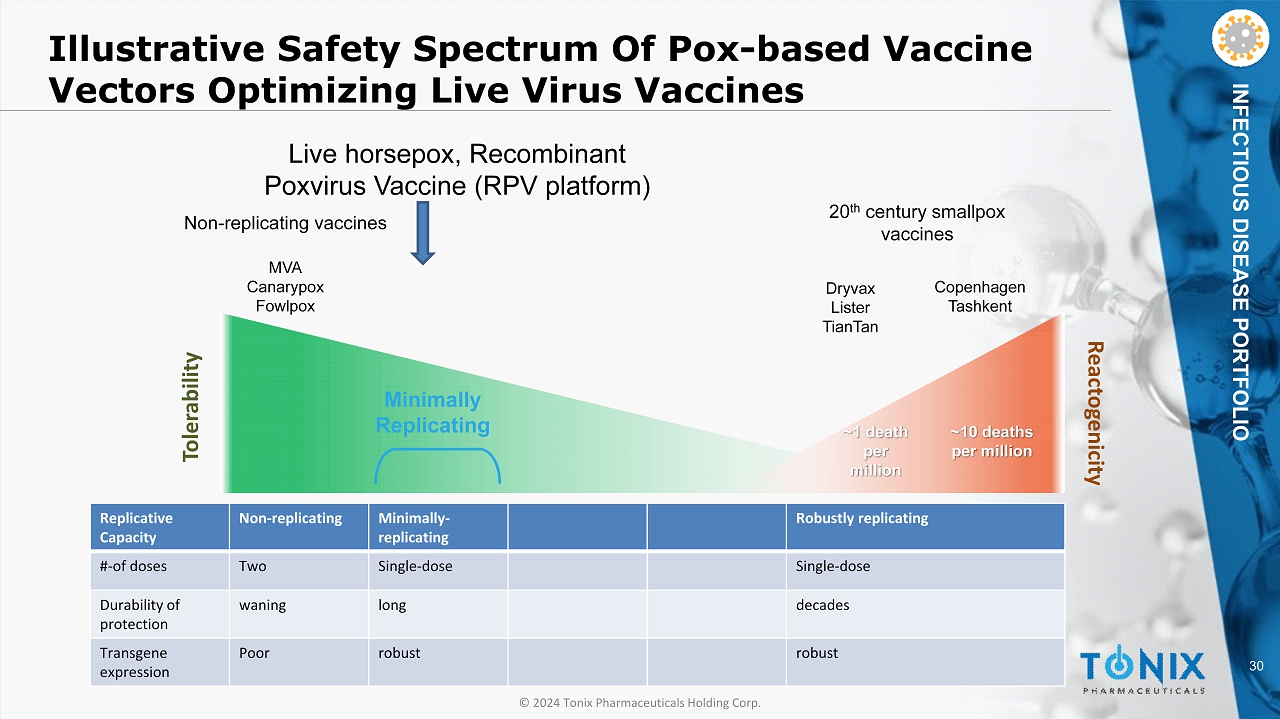
30 © 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. INFECTIOUS DISEASE PORTFOLIO Illustrative Safety Spectrum Of Pox - based Vaccine Vectors Optimizing Live Virus Vaccines ~1 death per million ~10 deaths per million 20 th century smallpox vaccines Dryvax Lister TianTan Copenhagen Tashkent MVA Canarypox Fowlpox Minimally Replicating Live horsepox, Recombinant Poxvirus Vaccine ( RPV platform ) Replicative Capacity Non - replicating Minimally - replicating Robustly replicating # - of doses Two Single - dose Single - dose Durability of protection waning long decades Transgene expression Poor robust robust Non - replicating vaccines Tolerability Reactogenicity

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Horsepox Protection and Tolerability in Animals Potentially Decouples Protective Immunity from Reactogenicity Conventional view holds that reactogenicity correlates with protection Protective immunity is not necessarily related to reactogenicity − Reactogenicity was a basis for testing vaccine activity prior to the understanding that vaccinia was a virus “Real World Evidence” supports efficacy of horsepox - like vaccines − Effectiveness of archaic vaccines (from the 1800’s or 19 th century) support the belief that horsepox will be protective against smallpox − Historical evidence that horsepox - like vaccines prevented forward transmission 1 Schrick, L. et al An Early American Smallpox Vaccine Based on Horsepox N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1491 2 Tulman ER, et al. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol ; 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 3 Brinkmann A et al, Genome Biol ogy 2020 ; 21:286 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059 - 020 - 02202 - 0 31

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Horsepox: More (Regulatory) Genes Confer Tolerability “20 th Century vaccinia vaccines” evolved through a process of “Passage” through cows or birds that was a primitive form of genetic engineering − “Passage” through cows resulted in gene deletions that may have increased virulence relative to “circa 1860 vaccinia” (20 th century “vaccinia” have deleted regulatory genes) − MVA: “Passage through birds resulted in extensive gene deletions that decreased replication in humans (“non - replicating”) Horsepox data: More Genes may be better than Fewer Genes − Horsepox appears to have preserved regulatory genes that confer tolerability, while preserving immune protection 1 Schrick, L. et al An Early American Smallpox Vaccine Based on Horsepox N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1491 2 Tulman ER, et al. Genome of horsepox virus. J Virol ; 2006 80(18):9244 - 58.PMID:16940536 3 Brinkmann A et al, Genome Biol ogy 2020 ; 21:286 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059 - 020 - 02202 - 0 32
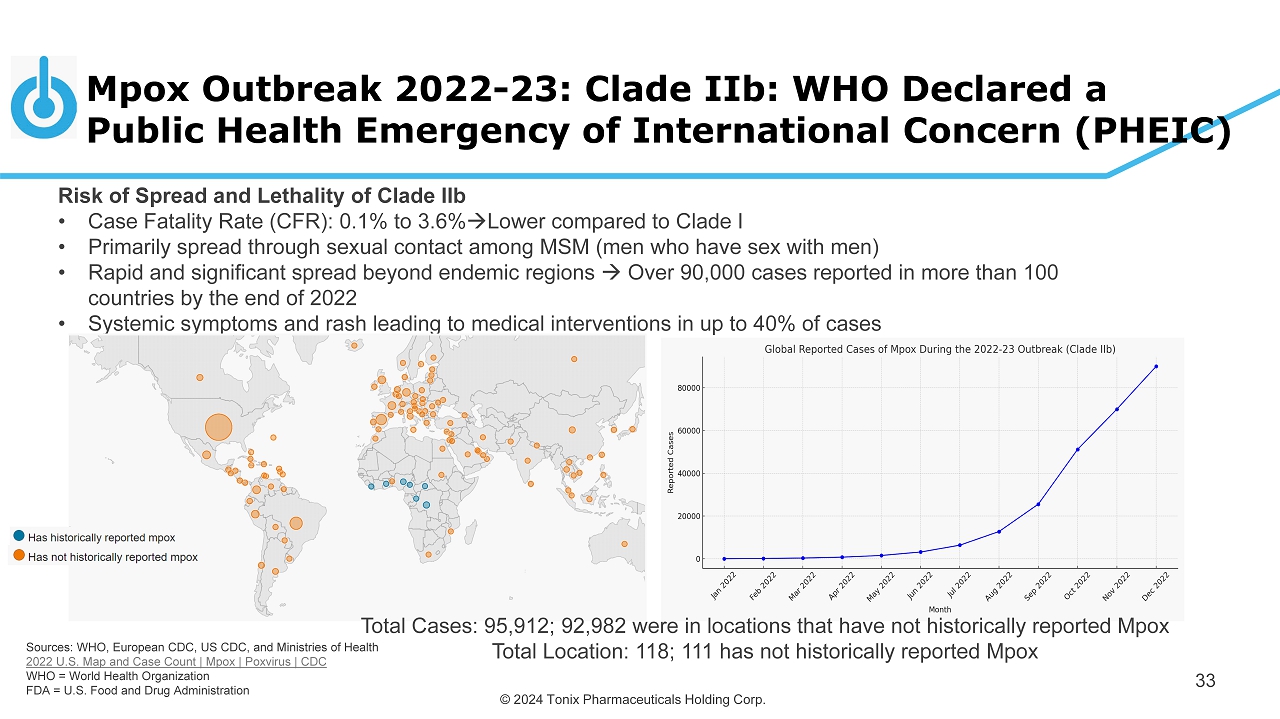
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Mpox Outbreak 2022 - 23: Clade IIb: WHO Declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) 33 Risk of Spread and Lethality of Clade IIb • Case Fatality Rate (CFR): 0.1% to 3.6% Lower compared to Clade I • Primarily spread through sexual contact among MSM (men who have sex with men) • Rapid and significant spread beyond endemic regions Over 90,000 cases reported in more than 100 countries by the end of 2022 • Systemic symptoms and rash leading to medical interventions in up to 40% of cases Sources: WHO, European CDC, US CDC, and Ministries of Health 2022 U.S. Map and Case Count | Mpox | Poxvirus | CDC WHO = World Health Organization FDA = U.S. Food and Drug Administration Total Cases: 95,912; 92,982 were in locations that have not historically reported Mpox Total Location: 118; 111 has not historically reported Mpox
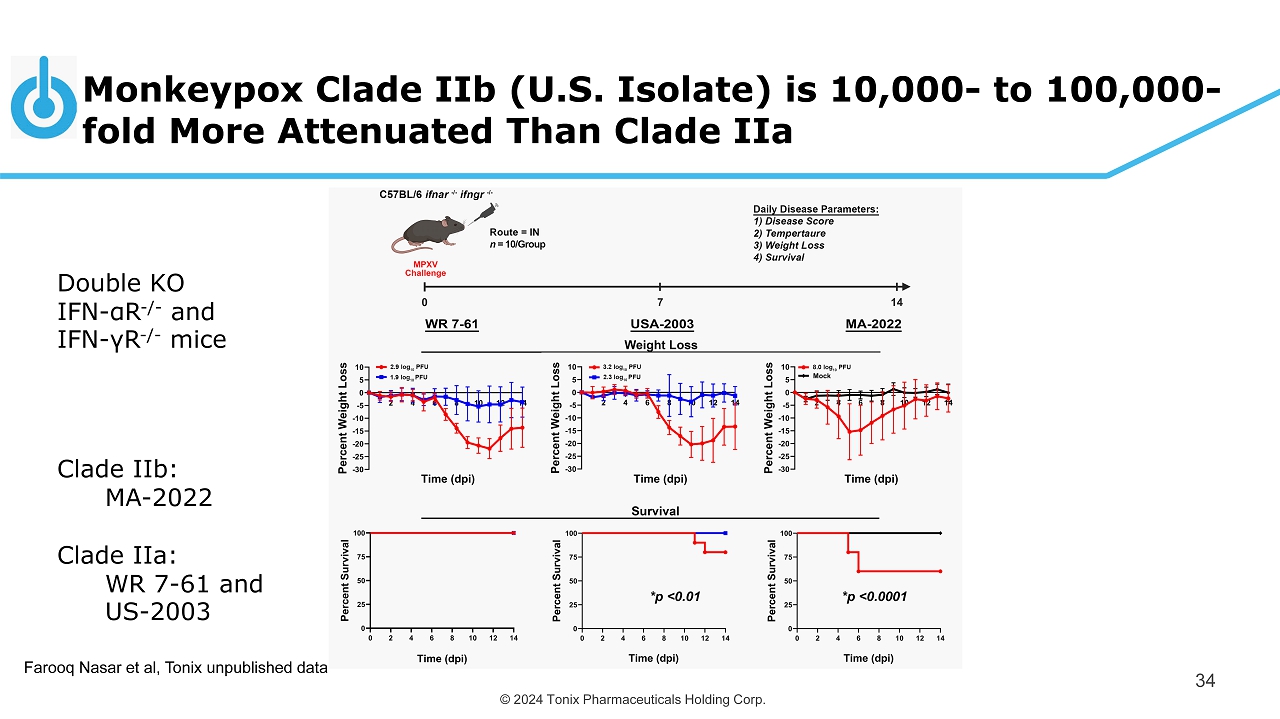
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Monkeypox Clade IIb (U.S. Isolate) is 10,000 - to 100,000 - fold More Attenuated Than Clade IIa 34 *p <0.0001 *p <0.01 Farooq Nasar et al, Tonix unpublished data Double KO IFN - α R - / - and IFN - γ R - / - mice Clade IIb: MA - 2022 Clade IIa : WR 7 - 61 and US - 2003
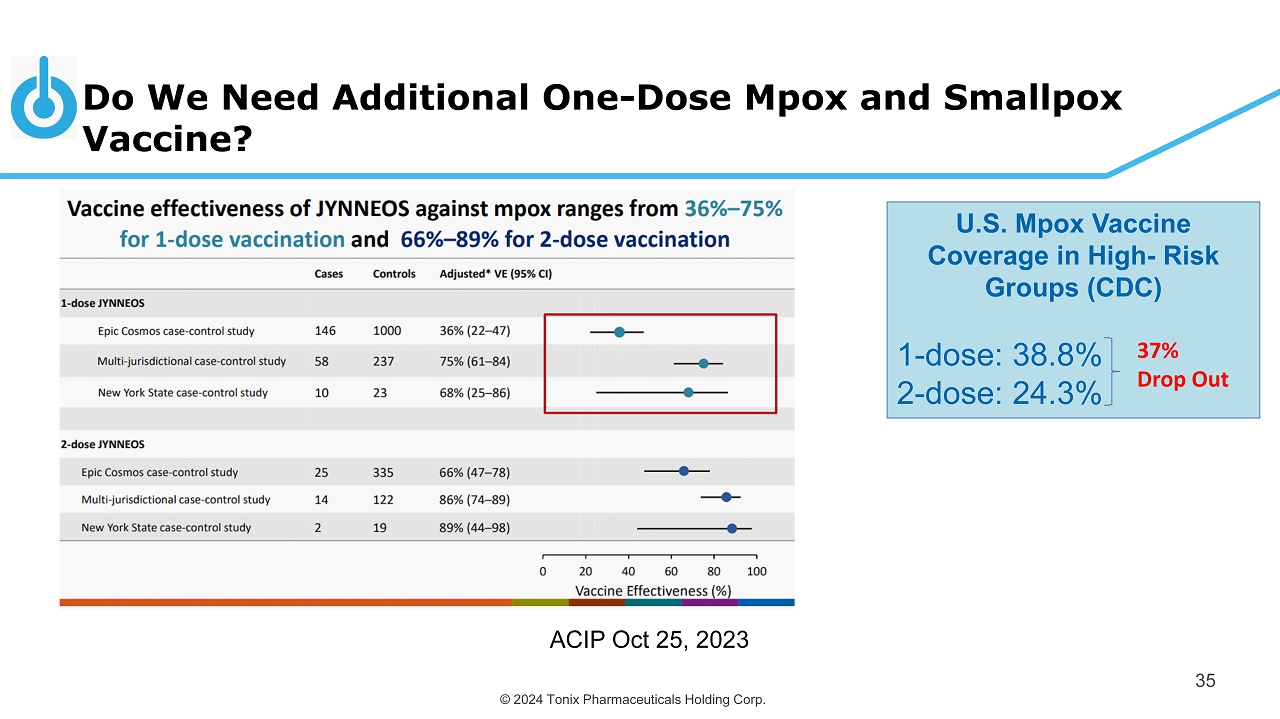
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Do We Need Additional One - Dose Mpox and Smallpox Vaccine? 35 ACIP Oct 25, 2023 U.S. Mpox Vaccine Coverage in High - Risk Groups (CDC) 1 - dose: 38.8% 2 - dose: 24.3% 37% Drop Out

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Mpox and Smallpox Reports by U.S. Agencies & Institutions • Multiple recent statements by U.S. Agencies warning about smallpox and monkeypox 1 - 6 • U.S. National Academy of Sciences Consensus Report (March, 2024) 6 ‒ “Additionally, safer, single - dose vaccines and a diverse set of therapeutic options against smallpox would improve the U.S. readiness and response posture for immediate containment and long - term protection in a smallpox emergency. ‒ “Smallpox vaccines that have improved safety across different population subgroups and are available as a single dose would support faster and more effective response to contain smallpox and other orthopoxvirus outbreaks. The development of novel smallpox vaccines using multi - vaccine platforms (i.e., use common vaccine vectors, manufacturing ingredients, and processes) would improve the capacity for rapid vaccine production in response to a smallpox event and reduce the need for stockpiling in the SNS at current levels. ‒ “Given the lack of commercially available orthopoxvirus diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics, planning for logistics and supply chain management considerations is critical. Efforts could give consideration to developing plans to increase the number of smallpox vaccine and therapeutics manufacturers as well as optimizing current manufacturing capacities should they be needed in the shorter term.” 1 Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP). American Pandemic Preparedness: Transforming Our Capabilities. September 2021 2 National Biodefense Science Board (NBSB). Prioritization of Product Attribute Categories to Maximize Access for Next Generati on COVID - 19 Vaccines and Therapeutics. August 2023 3 Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP). American Pandemic Preparedness: Transforming Our Capabilities. September 2021 4 National Biodefense Science Board (NBSB). Prioritization of Product Attribute Categories to Maximize Access for Next Generati on COVID - 19 Vaccines and Therapeutics. August 2023 5 BARDA Strategic Plan 2022 - 2026. 6 U.S. National Academy of Sciences. March 28, 2024. “Consensus Study Report: Future State of Smallpox Medical Countermeasures. ” https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/27652/future - state - of - smallpox - medical - countermeasures

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. U.S. Recognizes Smallpox Preparedness as a Priority National Stockpile Expansion is Recommended by Experts 37

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Mpox Outbreak 2023 - 24: Clade I and Current State of the Mpox Epidemic in Congo 38 Risk of Spread and Lethality • Higher CFRs 1.4% to over 10% • From January 1, 2023, to April 14, 2024, DRC reported 19,919 suspected cases and 975 deaths (4.9% CFR) in 25 out of 26 provinces • Children under 15 years old account for 70% of total cases and 88% of total deaths in DRC • Significant impact on sex workers in mining areas and LGBTQ+ communities • Global travel amplifies the spread of risk Number of suspected clade I Mpox cases, by province, DRC, January 1, 2023 – April 14, 2024 https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/73/wr/mm7319a3.htm C.D.C Warns of a Resurgence of Mpox A health official investigating and treating a probable case of Mpox at the Yalolia health center in Tshopo , DRC

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Mpox Declared Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by WHO* on August 14, 2024: New Clade I • Clade I - first wave in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) • ~10% mortality, • Affects children • Additional emerging mutation • Potentially lower mortality • Affects both MSM (men who have sex with men) + heterosexual transmission primarily in adults • 2024 mpox epidemic in DRC has led to >20,000 cases by mid - August • Spread to 12 countries in Africa, recently includes Kenya • First cases of Clade I identified in Sweden, Thailand, Singapore • Two FDA** - approved vaccines: • Jynneos ® (Bavarian - Nordic) • R equires 2 - dose regimen, durability of neutralization antibody titers being studied 1,2 • ACAM 2000 (Emergent) • Single - dose, reactogenic, provides durable protection 3 *WHO = World Health Organization **FDA = U.S. Food and Drug Administration 1 Zaeck LM, Nat Med. 2023 29(1):270 - 278. doi : 10.1038/s41591 - 022 - 02090 2 Berens - Riha N, et al. Euro Surveill . 2022 27(48):2200894. doi : 10.2807/1560 - 7917.ES.2022.27.48.2200894. 3 August 30, 2024. Reuters. “US FDA approves Emergent's smallpox vaccine for people at high risk of mpox”. https://www.msn.com/en - us/health/other/us - fda - approves - emergent - s - smallpox - vaccine - for - people - at - high - risk - of - mpox/
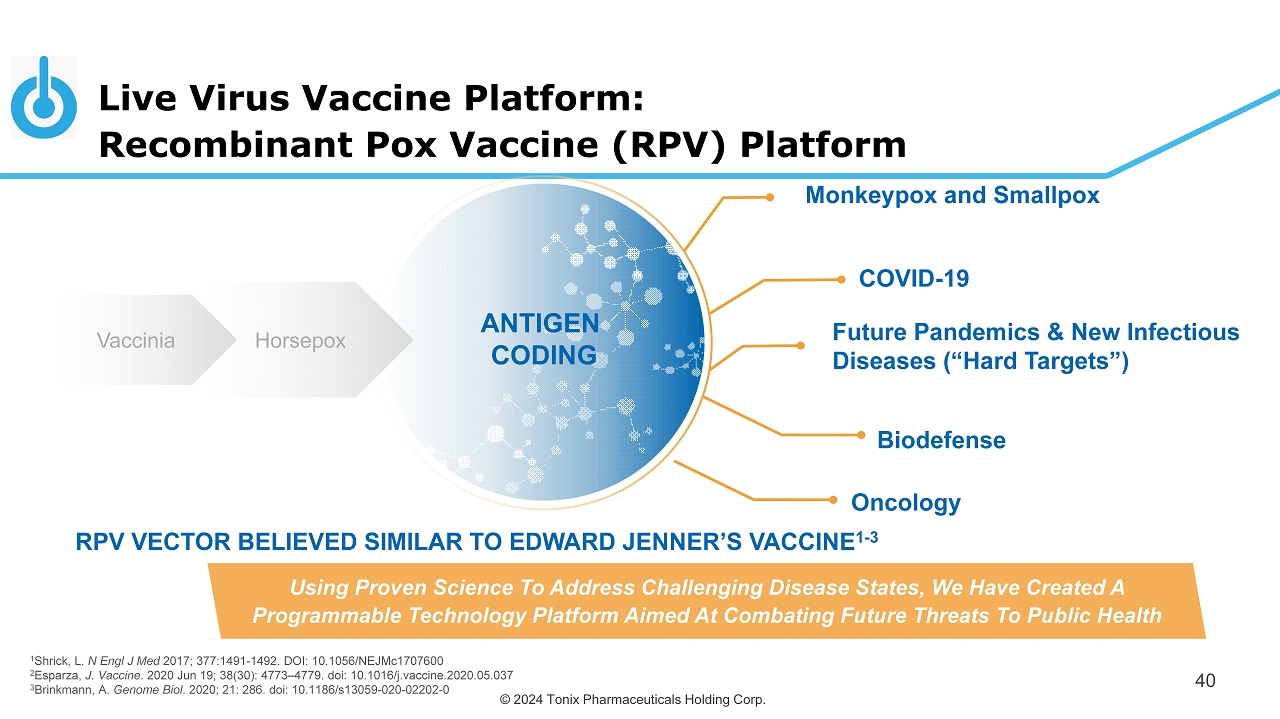
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Live Virus Vaccine Platform: Recombinant Pox Vaccine (RPV) Platform 40 Monkeypox and Smallpox Future Pandemics & New Infectious Diseases (“Hard Targets”) COVID - 19 Biodefense Using Proven Science To Address Challenging Disease States, We Have Created A Programmable Technology Platform Aimed At Combating Future Threats To Public Health Vaccinia Horsepox ANTIGEN CODING Oncology RPV VECTOR BELIEVED SIMILAR TO EDWARD JENNER’S VACCINE 1 - 3 1 Shrick, L. N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1491 - 1492. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc1707600 2 Esparza, J. Vaccine . 2020 Jun 19; 38(30): 4773 – 4779. doi : 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.037 3 Brinkmann, A. Genome Biol . 2020; 21: 286. doi : 10.1186/s13059 - 020 - 02202 - 0

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 1800 (SARS - CoV - 2 spike – Expressing HPXV) Immunogenicity in Hamsters and Rabbits - 2023 41 Awasthi M, et al. Viruses . 2023 Oct 21;15(10):2131. doi : 10.3390/v15102131. PMID: 37896908; PMCID: PMC10612059.
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Recombinant SARS - CoV - 2 Vaccine Generation (TNX - 1800* Expresses Spike) 42 Development of HPXV as a recombinant Delivery Vector Platform Central General Region 36Kp - 146Kbp Left Terminal Region 60Kbp Right Terminal Region 147 - 212 kbp Essential Viral Genes Non - Essential Viral Genes L - ITR Non - Essential Viral Genes R - ITR HPXV Genes 001 - 062 HPXV Genes 063 - 145 HPXV Genes 146 - 207 Δ095 (TK) Pox E/L Promotor Right Flanking Arm Left Flanking Arm Recombinant Generation Rescue virus: TNX - 1800 SARS - CoV - 2 WA - 2020 Spike Protein Gene *TNX - 1800 has not been approved for any indication.
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 1800 Immunogenicity and Efficacy in NHPs - 2023 43 Awasthi M, et al. Viruses . 2023 Oct 21;15(10):2131. doi : 10.3390/v15102131. PMID: 37896908; PMCID: PMC10612059.
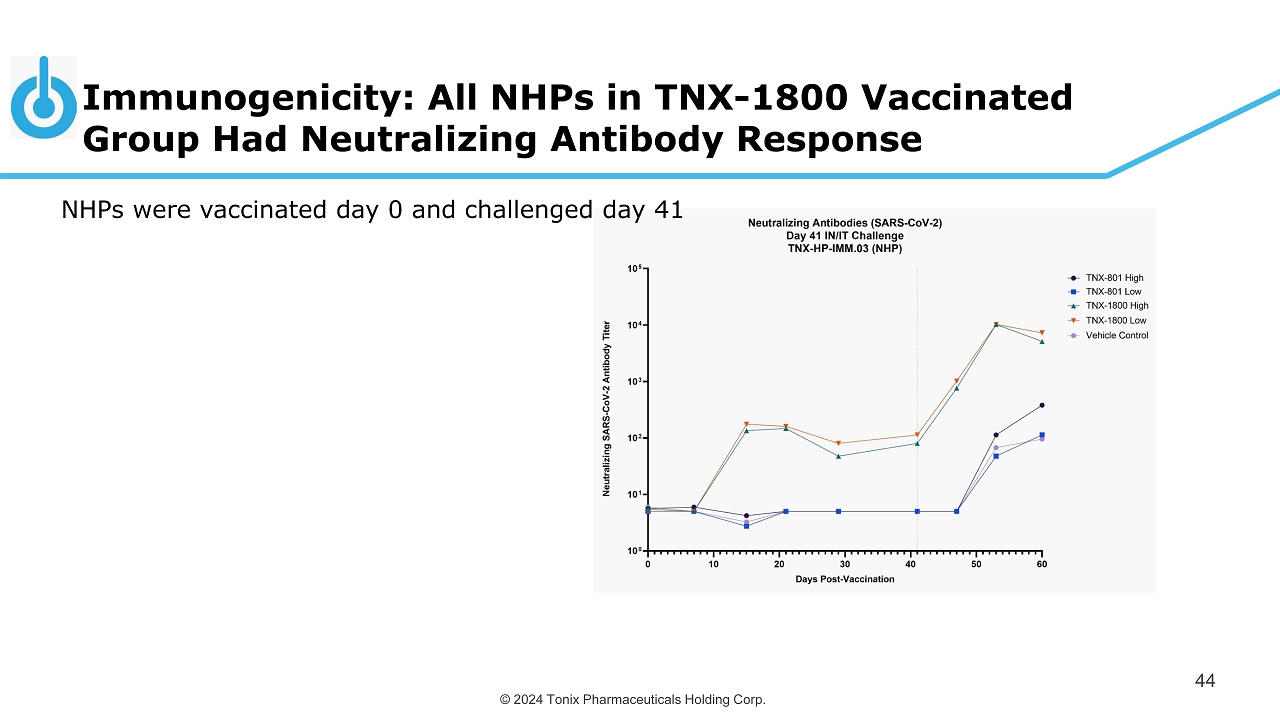
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. T N X - 1 8 0 0 D i l u e n t T N X - 1 8 0 0 D i l u e n t T N X - 1 8 0 0 D i l u e n t T N X - 1 8 0 0 D i l u e n t T N X - 1 8 0 0 D i l u e n t T N X - 1 8 0 0 D i l u e n t 0 100 200 300 400 M i c r o n e u t r a l i z a t i o n T i t e r -1 Days Post-Vaccination 7 14/15 21 28/29 41 Immunogenicity: All NHPs in TNX - 1800 Vaccinated Group Had Neutralizing Antibody Response 44 NHPs were vaccinated day 0 and challenged day 41
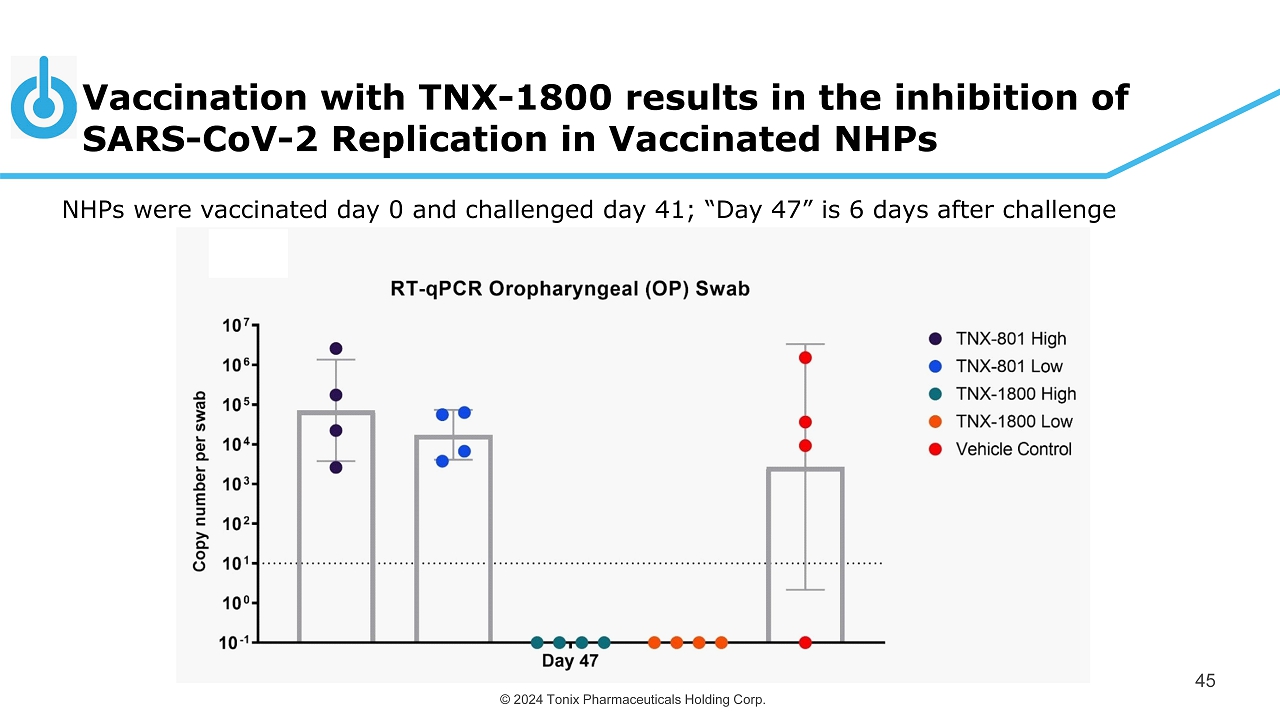
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Vaccination with TNX - 1800 results in the inhibition of SARS - CoV - 2 Replication in Vaccinated NHPs 45 NHPs were vaccinated day 0 and challenged day 41; “Day 47” is 6 days after challenge

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. TNX - 801 is Potential Vaccine for Mpox and Smallpox Platform to express other viral antigens Animal studies show TNX - 801 protects against mpox − Appears to provide mucosal immunity after percutaneous vaccination (May prevent forward transmission) Single dose efficacy − May elicit durable or long - term protection by stimulating T cell (“cell - mediated”) immunity Economical to manufacture at scale − Low dose because replication amplifies dose in vivo Standard cold chain believed to be sufficient for shipping and storage Jenner’s vaccinia is the oldest vaccine technology – can now be engineered with payload antigens − “Jenner’s vaccinia” and its descendants “circa 1960 Vaccinia” eradicated smallpox − “20 th century vaccinia” kept mpox out of the human population in Africa − Horsepox and vaccinia express transgenes with high fidelity 46

© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Tonix Platform Selected by NIH/NIAID : Project NextGen COVID 47

48 © 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. INFECTIOUS DISEASE PORTFOLIO TNX - 801: Pre - IND Ready Candidate Mpox Vaccine • Based on synthetic horsepox - vector, believed related to first smallpox vaccine reported by Dr. Edward Jenner in 1798 • Single - dose percutaneous • Attenuated live virus for durable T - cell immunity • Believed will be thermo - stable in ultimate lyophilized formulation • Eventual presentation may use Micro Array Patch technology R&D Center - Maryland Operational BSL - 3 capable Advanced Manufacturing Center - MA GMP - manufacturing capability* *GMP Suites currently decommissioned
© 2024 Tonix Pharmaceuticals Holding Corp. Contributors 49 Tonix Christy Raney Amy Cregger Chase A. Gonzales Brittany Layton Robert Enamorado Nelson Martinez Deborah Gohegan Massoudeh Masoud - Bahamiri Jennifer Cho Dawn Myscofski Tinoush Moulaei Nastasza Ziółkowska Current Addresses 1 McKinsey 2 University of Pennsylvania 3 IITRI 4 National Toxicology Program (NTP) at National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), NIH; Artic Slope Regional C orp . Univ. of Maryland – Institute of Human Virology José Esparza Univ. of Alberta Ryan Noyce David Evans Southern Research Fusataka Koide Landon Westfall 3 Karen Gilbert 4 LINQ Pharma Consulting Onesmo Mpanju Tonix Seth Lederman Sina Bavari Scott Goebel Farooq Nasar Zeil Rosenberg Siobhan Fogarty Mayanka Awasthi Stephanie Trefry Bruce Daugherty Sarah Brinckmann 1 Helen Stillwell 2